Dynamic LTR retrotransposon transcriptome landscape in septic shock patients
- PMID: 32188504
- PMCID: PMC7081582
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-020-2788-8
Dynamic LTR retrotransposon transcriptome landscape in septic shock patients
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is defined as a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. Numerous studies have explored the complex and dynamic transcriptome modulations observed in sepsis patients, but a large fraction of the transcriptome remains unexplored. This fraction could provide information to better understand sepsis pathophysiology. Multiple levels of interaction between human endogenous retroviruses (HERV) and the immune response have led us to hypothesize that sepsis is associated with HERV transcription and that HERVs may contribute to a signature among septic patients allowing stratification and personalized management.
Methods: We used a high-density microarray and RT-qPCR to evaluate the HERV and Mammalian Apparent Long Terminal Repeat retrotransposons (MaLR) transcriptome in a pilot study that included 20 selected septic shock patients, stratified on mHLA-DR expression, with samples collected on day 1 and day 3 after inclusion. We validated the results in an unselected, independent cohort that included 100 septic shock patients on day 3 after inclusion. We compared septic shock patients, according to their immune status, to describe the transcriptional HERV/MaLR and conventional gene expression. For differential expression analyses, moderated t tests were performed and Wilcoxon signed-rank tests were used to analyze RT-qPCR results.
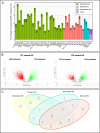
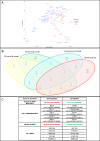
Results: We showed that 6.9% of the HERV/MaLR repertoire was transcribed in the whole blood, and septic shock was associated with an early modulation of a few thousand of these loci, in comparison to healthy volunteers. We provided evidence that a subset of HERV/MaLR and conventional genes were differentially expressed in septic shock patients, according to their immune status, using monocyte HLA-DR (mHLA-DR) expression as a proxy. A group of 193 differentially expressed HERV/MaLR probesets, tested in an independent septic shock cohort, identified two groups of patients with different immune status and severity features.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that a large, unexplored part of our genome, which codes for HERV/MaLR, may be linked to the host immune response. The identified set of HERV/MaLR probesets should be evaluated on a large scale to assess the relevance of these loci in the stratification of septic shock patients. This may help to address the heterogeneity of these patients.
Keywords: HERV transcriptome; Immunosuppression; Septic shock patients; Whole blood; mHLA-DR expression.
Conflict of interest statement
MM, AG, GO, EC, VC, AP, KBP, JT, and FM are employees of bioMérieux, an in vitro diagnostic company. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Monneret G, Finck ME, Venet F, Debard AL, Bohe J, Bienvenu J, Lepape A. The anti-inflammatory response dominates after septic shock: association of low monocyte HLA-DR expression and high interleukin-10 concentration. Immunol Lett. 2004;95(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2004.07.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

