Autologous platelet-rich derivatives along with alloplastic bone substitute in the management of complex perio-endo cases
- PMID: 32189849
- PMCID: PMC7069109
- DOI: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_81_19
Autologous platelet-rich derivatives along with alloplastic bone substitute in the management of complex perio-endo cases
Abstract
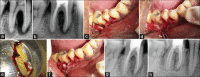
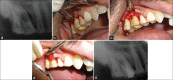
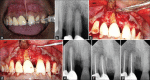
Combined endodontic periodontal lesion is one of the most challenging dental conditions as making a definite diagnosis and henceforth treatment plan is a daunting task. The prognosis of complex lesion involving both endodontic and periodontic components is complex, but success rate can be improved with regenerative therapies. However, there is paucity of literature regarding its effectiveness in the clinical scenario as only few case reports have been documented in literature for the use of platelet-rich derivatives in regenerative osseous surgery requiring both endodontic and periodontal treatment. We are hereby presenting three cases requiring both endo and perio treatment. The first two cases involve mandibular first molar and maxillary first molar, respectively. The third case involves maxillary central incisor. In all the cases, first, endodontic treatment was initiated, then open flap curettage along with alloplastic bone substitutes was done. Platelet-rich fibrin and platelet-rich plasma were used along with. Three of the treated cases showed significant improvement radiographically and clinically. There was gain in clinical attachment, reduction in probing depth, and radiographic bone fill. Autologous platelet-rich derivative can be used in combination with alloplastic bone substitute for the management of endo-perio cases. Further long-term studies are needed to explore the clinical effectiveness of platelet-rich derivatives and predicting the probability of success of periodontal therapy.
Keywords: Bone graft; bone regeneration; furcation; root canal.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical effectiveness of combining platelet rich fibrin with alloplastic bone substitute for the management of combined endodontic periodontal lesion.Restor Dent Endod. 2014 Feb;39(1):51-5. doi: 10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.51. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Restor Dent Endod. 2014. PMID: 24516830 Free PMC article.
-
Management of an endo perio lesion in a maxillary canine using platelet-rich plasma concentrate and an alloplastic bone substitute.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2009 May;13(2):97-100. doi: 10.4103/0972-124X.55839. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2009. PMID: 20407658 Free PMC article.
-
A sequential approach in treatment of perio-endo lesion.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2011 Apr;15(2):177-80. doi: 10.4103/0972-124X.84390. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2011. PMID: 21976845 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Efficacy of Treatment of Endodontic-Periodontal Lesions: A Systematic Scoping Review of Experimental Studies.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 21;19(20):13649. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192013649. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36294232 Free PMC article.
-
Autologous Platelet Concentrates in Treatment of Furcation Defects-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 17;20(6):1347. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061347. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30884920 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Expert consensus on the diagnosis and therapy of endo-periodontal lesions.Int J Oral Sci. 2024 Sep 1;16(1):55. doi: 10.1038/s41368-024-00320-0. Int J Oral Sci. 2024. PMID: 39217161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-rich fibrin and titanium-prepared platelet-rich fibrin in endoperio lesion management.Bioinformation. 2023 Jan 31;19(1):133-137. doi: 10.6026/97320630019133. eCollection 2023. Bioinformation. 2023. PMID: 37720281 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of an Endo-Perio Lesion with Ozone Gas in a Patient with Aggressive Periodontitis: A Clinical Case Report and Literature Review.Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2020 Oct 28;12:447-464. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S267933. eCollection 2020. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2020. PMID: 33149696 Free PMC article.
-
An interdisciplinary approach for the management of periapical lesion using regenerative approach: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2025 Jul 9;19(1):333. doi: 10.1186/s13256-025-05380-2. J Med Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40635079 Free PMC article.
-
B.P.F.C.® Bio-Plasma® with Pure Growth Factors (BioPlasma®) Used for the Treatment of a Persistent Great Periapical Lesion of an Endodontically Treated Tooth: A New Therapeutic Option.Case Rep Dent. 2020 Jun 29;2020:4876437. doi: 10.1155/2020/4876437. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Dent. 2020. PMID: 32685218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hirsch JM, Ahlström U, Henrikson PA, Heyden G, Peterson LE. Periapical surgery. Int J Oral Surg. 1979;8:173–85. - PubMed
-
- Imura N, Pinheiro ET, Gomes BP, Zaia AA, Ferraz CC, Souza-Filho FJ. The outcome of endodontic treatment: A retrospective study of 2000 cases performed by a specialist. J Endod. 2007;33:1278–82. - PubMed
-
- Meschi N, Castro AB, Vandamme K, Quirynen M, Lambrechts P. The impact of autologous platelet concentrates on endodontic healing: A systematic review. Platelets. 2016;27:613–33. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
