Mitigation of Rheumatic Arthritis in a Rat Model via Transdermal Delivery of Dapoxetine HCl Amalgamated as a Nanoplatform: In vitro and in vivo Assessment
- PMID: 32189966
- PMCID: PMC7065716
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S238709
Mitigation of Rheumatic Arthritis in a Rat Model via Transdermal Delivery of Dapoxetine HCl Amalgamated as a Nanoplatform: In vitro and in vivo Assessment
Abstract
Purpose: Dapoxetine HCl (DH), a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, may be useful for the treatment of rheumatic arthritis (RA). The purpose of this study was to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of transdermal delivery of DH in transethosome nanovesicles (TENVs). This novel delivery of DH may overcome the drawbacks associated with orally administered DH and improve patient compliance.
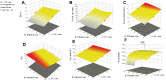
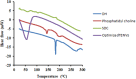
Methods: DH-TENV formulations were prepared using an injection- sonication method and optimized using a 33 Box-Behnken-design with Design Expert® software. The TENV formulations were assessed for entrapment efficiency (EE-%), vesicle size, zeta potential, in vitro DH release, and skin permeation. The tolerability of the optimized DH-TENV gel was investigated using a rat skin irritation test. A pharmacokinetic analysis of the optimized DH-TENV gel was also conducted in rats. Moreover, the anti-RA activity of the optimized DH-TENV gel was assessed based on the RA-specific marker anti-cyclic cirtullinated peptide antibody (anti-CCP), the cartilage destruction marker cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) and the inflammatory marker interleukin-6 (IL-6). Level of tissue receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand (RANKL) were also assessed.
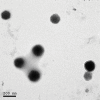
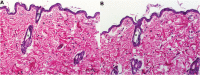
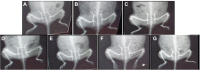
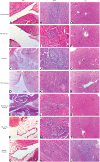
Results: The optimized DH-TENV formulation involved spherical nanovesicles that had an appropriate EE- % and skin permeation characteristic. The DH-TENV gel was well tolerated by rats. The pharmacokinetics analysis showed that the optimized DH-TENV gel boosted the bioavailability of the DH by 2.42- and 4.16-fold compared to the oral DH solution and the control DH gel, respectively. Moreover, it significantly reduced the serum anti-CCP, COMP and IL-6 levels and decreased the RANKL levels. Furthermore, the DH-TENV gel attenuated histopathological changes by almost normalizing the articular surface and synovial fluid.
Conclusion: The results indicate that DH-TENVs can improve transdermal delivery of DH and thereby alleviate RA.
Keywords: RANKL; SSRIs; autoimmune disease; nano carrier via skin; pharmacokinetic parameters.
© 2020 Salem et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Dapoxetine HCl by Nano-Vesicle Transdermal Gel for Treatment of Carrageenan-Induced Rat Paw Edema.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020 Apr 14;21(3):113. doi: 10.1208/s12249-020-01656-6. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020. PMID: 32291553
-
Topical Nano-Vesicular Spanlastics of Celecoxib: Enhanced Anti-Inflammatory Effect and Down-Regulation of TNF-α, NF-кB and COX-2 in Complete Freund's Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis Model in Rats.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jan 8;16:133-145. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S289828. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33447032 Free PMC article.
-
Development and optimization of nanoemulsion based gel for enhanced transdermal delivery of nitrendipine using box-behnken statistical design.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2020 Feb;46(2):329-342. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2020.1721527. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31976777
-
Deep-insights: Nanoengineered gel-based localized drug delivery for arthritis management.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2025 Feb;20(1):101012. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2024.101012. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 39995751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-rheumatic effect of quercetin and recent developments in nano formulation.RSC Adv. 2021 Feb 11;11(13):7280-7293. doi: 10.1039/d0ra08817j. eCollection 2021 Feb 10. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35423269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advancement in nanotechnology for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: scope and potential applications.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Oct;396(10):2287-2310. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02514-5. Epub 2023 May 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37166463 Review.
-
(+)-Erythro-Δ8'-7S,8R-Dihydroxy-3,3',5'-Trimethoxy-8-O-4'-Neolignan, an Anti-Acne Component in Degreasing Myristica fragrans Houtt.Molecules. 2020 Oct 6;25(19):4563. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194563. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33036279 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Evaluation of Imatinib Loaded Transfersomal gel for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Iran J Pharm Res. 2021 Fall;20(4):33-46. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2021.115481.15394. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 35194426 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication and Appraisal of Simvastatin via Tailored Niosomal Nanovesicles for Transdermal Delivery Enhancement: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jan 21;13(2):138. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020138. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33494472 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the Therapeutic Effect and Bioavailability of Irradiated Silver Nanoparticle-Capped Chitosan-Coated Rosuvastatin Calcium Nanovesicles for the Treatment of Liver Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jan 7;17(1):72. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17010072. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 39861720 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

