Potential application of lutetium-177-labeled prostate-specific membrane antigen-617 radioligand therapy for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in a limited resource environment: Initial clinical experience after 2 years
- PMID: 32190017
- PMCID: PMC7067127
- DOI: 10.4103/wjnm.WJNM_20_19
Potential application of lutetium-177-labeled prostate-specific membrane antigen-617 radioligand therapy for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in a limited resource environment: Initial clinical experience after 2 years
Abstract
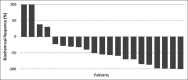
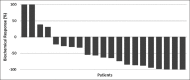
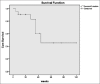
In recent years, lutetium-177 (177Lu)-labeled prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-617 has become a promising new therapeutic agent in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). In this study, we report on an early experience of 177Lu-PSMA therapy with an evaluation of its efficacy and safety in mCRPC patients. Twenty-one mCRPC patients with a mean age of 70.3 ± 9.6 (54-88)-year-old were treated with one to four therapy cycles (median two cycles) and administered activity of 3.7-29.6 GBq (mean of 15.4 GBq). A prostate-specific antigen (PSA) decline ≥ 50% was considered to be a biochemical response (BCR). To evaluate the clinical response, the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) status was used. Within 2 weeks before and 1 and 2 months after each therapy cycle, hematology, renal function, liver status, alkaline phosphatase, and PSA were checked. The Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events was used for grading adverse events induced by 177Lu-PSMA. Furthermore, overall survival (OS) was calculated and analyzed. During the treatment, a BCR was seen in 62% of patients; 19% of patients showed progression and 19% of patients showed stable disease. ECOG status was improved after treatment, and OS was 62.7 weeks. After the treatment, two patients showed Grade II toxicity of white blood cells, Grade I thrombocytopenia was observed in two patients, one patient showed Grade II toxicity in serum creatinine and transient Grade I toxicity in creatinine was seen in two patients. In total, our initial experience demonstrates that 177Lu-PSMA therapy has the potential to positively affect the development and maturation of radioligand practices in selected mCRPC patients, even in resource limited, developing country environments. However, some challenges, such as practitioner training, poor initial acceptance by colleagues and financial concerns, particularly in developing nations, still exist.
Keywords: Biochemical response; lutetium-177 -prostate-specific membrane antigen; prostate cancer; radioligand therapy; toxicity.
Copyright: © 2020 World Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Center MM, Jemal A, Lortet-Tieulent J, Ward E, Ferlay J, Brawley O, et al. International variation in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates. Eur Urol. 2012;61:1079–92. - PubMed
-
- Hofman MS, Violet J, Hicks RJ, Ferdinandus J, Thang SP, Akhurst T, et al. [177Lu]-PSMA-617 radionuclide treatment in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (LuPSMA trial): A single-centre, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:825–33. - PubMed
-
- Wei Q, Li M, Fu X, Tang R, Na Y, Jiang M, et al. Global analysis of differentially expressed genes in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2007;10:167–74. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

