Simultaneous Determination of 13 Constituents of Radix Polygoni Multiflori in Rat Plasma and Its Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study
- PMID: 32190053
- PMCID: PMC7072103
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4508374
Simultaneous Determination of 13 Constituents of Radix Polygoni Multiflori in Rat Plasma and Its Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study
Abstract
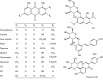
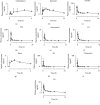
Radix Polygoni Multiflori (RPM) has been widely used to treat various diseases in Asian countries for many centuries. Although, stilbenes and anthraquinones, two major components of RPM, show various bioactive effects, it has been speculated that the idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity induced by RPM may be related to these constituents. However, information on the pharmacokinetics of stilbenes and anthraquinones at a subtoxic dose of RPM is limited. A simple and sensitive UPLC-MS/MS bioanalytical method for the simultaneous determination of 13 ingredients of RPM, including chrysophanol, emodin, aloe-emodin, rhein, physcion, questin, citreorosein, questinol, 2,3,5,4'-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside, torachrysone-8-O-glucoside, chrysophanol-8-O-β-D-glucoside, emodin-8-O-β-D-glucoside, and physcion-8-O-β-D-glucoside, in rat plasma was established. Acetonitrile was employed to precipitate the plasma with appropriate sensitivity and acceptable matrix effects. Chromatographic separation was performed using a waters HSS C18 column with a gradient elution using water and acetonitrile both containing 0.025% formic acid within a run time of 9 min. The constituents were detected in negative ionization mode using multiple reaction monitoring. The method was fully validated in terms of selectivity, linearity, accuracy, precision, recovery, matrix effects, and stability. The lower limit of quantitation of the analytes was 0.1-1 ng/mL. The intrabatch and interbatch accuracies were 87.1-109%, and the precision was within the acceptable limits. The method was applied to a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of RPM extract to rats at a subtoxic dose of 36 g/kg.
Copyright © 2020 Wenhao Cheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Vol. 1. Beijing, China: China Medical Science and Technology Press; 2005.
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Vol. 1. Beijing, China: China Medical Science and Technology Press; 2010.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

