Corallodiscus flabellata B.L. Burtt Extracts Stimulate Diuretic Activity and Regulate the Renal Expression of Aquaporins
- PMID: 32190088
- PMCID: PMC7064869
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6020817
Corallodiscus flabellata B.L. Burtt Extracts Stimulate Diuretic Activity and Regulate the Renal Expression of Aquaporins
Abstract
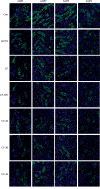
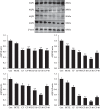
Corallodiscus flabellata B. L. Burtt is a traditional Chinese medicine. Previous studies in our laboratory showed that C. flabellata alleviated symptoms of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in a rat model of AD and increased healthy rats' urine volume. The aims of this study were to explore the diuretic activity of different extracts from C. flabellata and to identify the underlying mechanisms of action. Different doses of a C. flabellata extract (CF-L, CF-M, and CF-H) were administered orally to male KM mice in a single dose. In another procedure, C. flabellata (CF), water extract, and 20%, 30%, and 40% ethanol extracts of C. flabellata (CF-WE, CF-20, CF-30, and CF-40) were administered orally daily for 5 days. The urinary excretion rate, osmolality, and electrolyte levels in urine and serum, renal expression of aquaporins (AQPs), apoptosis-related protein, and MAPK-related protein were analyzed. The results showed that single doses of CF-M and CF-H increased urinary volume significantly, as well as daily administration of CF, CF-WE, CF-20, CF-30, and CF-40. Furthermore, CF-20 and CF-30 increased the concentration of Na+ in the urine. Treatment with CF-40 increased the urine osmolality and Na+ and Cl- concentrations and decreased the concentration of Na+ in the serum. Also, CF, CF-WE, CF-20, CF-30, and CF-40 decreased the renal expression of AQPs, as well as the ratios of Bcl-2/Bax, p-ERK/ERK, p-JNK/JNK, and p-p38/p38. In sum, the medium and high doses of the C. flabellata extract and CF-WE, CF-20, CF-30, and CF-40 were found to have a diuretic activity. They may inhibit the renal expression of AQPs and apoptosis-related proteins by inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway, thereby achieving diuretic effects.
Copyright © 2020 Yuxuan Kan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Extract of Corallodiscus flabellata attenuates renal fibrosis in SAMP8 mice via the Wnt/β-catenin/RAS signaling pathway.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Feb 28;22(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03535-y. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35227255 Free PMC article.
-
Corallodiscus flabellata B. L. Burtt extract alleviates lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure and brain injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Nov;23(11):1445-1452. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.45437.10567. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33235702 Free PMC article.
-
Corallodiscus flabellata B. L. Burtt extract and isonuomioside A ameliorate Aβ25-35-induced brain injury by inhibiting apoptosis, oxidative stress, and autophagy via the NMDAR2B/CamK Ⅱ/PKG pathway.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jul;101:154114. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154114. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35489325
-
Two polyphenols isolated from Corallodiscus flabellata B. L. Burtt ameliorate amyloid β-protein induced Alzheimer's disease neuronal injury by improving mitochondrial homeostasis.Behav Brain Res. 2023 Feb 25;440:114264. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2022.114264. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Behav Brain Res. 2023. PMID: 36535434
-
Lagopsis supina exerts its diuretic effect via inhibition of aquaporin-1, 2 and 3 expression in a rat model of traumatic blood stasis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Mar 1;231:446-452. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.10.034. Epub 2018 Oct 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30394291
Cited by
-
Extract of Corallodiscus flabellata attenuates renal fibrosis in SAMP8 mice via the Wnt/β-catenin/RAS signaling pathway.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Feb 28;22(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03535-y. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35227255 Free PMC article.
-
Corallodiscus flabellata B. L. Burtt extract alleviates lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure and brain injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Nov;23(11):1445-1452. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.45437.10567. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33235702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zheng X. K., Li J., Feng W. S., Bi Y. F., Ji C. R. Studies on the chemical constituents from Herba of Corallodiscus flabellata. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 2002;27(12):926–928. - PubMed
-
- Zheng X. K., Li J., Feng W. S., et al. Isolation and Structure Identification of phenylethanoid glycosides from Corallodiscus flabellate B.L. Burtt. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. 2003;2:116–119. - PubMed
-
- Yao Y. Study on the Chemical Constituents and Their Tyrosinase Inhibition of Corallodiscus Flabellatus. Kunming, China: Kunming University of Science and Technology; 2012.
-
- Shao Y., Wu Q. N., Yue W., et al. Research progress on C-glycosylflavones for protection of myocardial ischemia. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs. 2015;46(1):128–139.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

