Protective effects of synbiotic soymilk fortified with whey protein concentrate and zinc sulfate against bile duct ligated-induced hepatic encephalopathy
- PMID: 32190227
- PMCID: PMC7069541
Protective effects of synbiotic soymilk fortified with whey protein concentrate and zinc sulfate against bile duct ligated-induced hepatic encephalopathy
Abstract
Aim: This study aimed to compare the effects of synbiotic soymilk fortified with whey protein concentrate and zinc sulfate with lactulose on bile duct ligated-induced HE.
Background: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is seriously associated with neuromuscular and cognitive alterations.
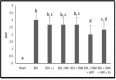
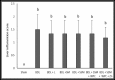
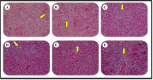
Methods: Eighty-two Sprague Dawley rats were randomly assigned into seven groups (sham, bile duct ligation (BDL), BDL + lactulose, BDL + soymilk (SM), BDL + Synbiotic soymilk (SSM), BDL + SSM + whey protein concentrate (WPC), BDL + SSM + WPC + ZnSO4). Different SM products, lactulose, and normal saline were administered via oral gavage (2 mL/rat/day). The serum and liver markers as well as liver histopathology were assessed after 28 days.
Results: The SM products significantly reduced the serum alanine aminotransferase, albumin, and ammonia (P < 0.05). The levels of aspartate aminotransferase, endotoxin, and liver interleukin-6 improved significantly in all treatments, except for those receiving SM. SSM and SSM + WPC + ZnSO4 were the only effective products in reducing serum alkaline phosphatase (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the liver total antioxidant capacity was greater (P<0.05) in the SSM + WPC and SSM + WPC + ZnSO4 groups. The histopathological examinations confirmed the efficiency of all SM products in reducing liver fibrosis. Liver bile duct proliferation diminished only in the SSM + WPC and SSM + WPC+ ZnSO4 groups (P<0.05).
Conclusion: This study showed the positive effects of different SM products, especially SSM + WPC and SSM + WPC + ZnSO4, on HE. Further studies are required to confirm our findings.
Keywords: Hepatic encephalopathy; Soymilk; Synbiotic; Whey protein; Zinc sulfate.
©2020 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Protective effect of gastrodin on bile duct ligation-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2015 Dec;86:202-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2015.10.010. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 26498411
-
Effect of Rifaximin on Hepatic Fibrosis in Bile Duct-ligated Rat Model.Korean J Gastroenterol. 2017 Nov 25;70(5):239-246. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2017.70.5.239. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29161793
-
Sex is associated with differences in oxidative stress and susceptibility to severe hepatic encephalopathy in bile-duct ligated rats.J Neurochem. 2022 Aug;162(4):337-351. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15661. Epub 2022 Jul 18. J Neurochem. 2022. PMID: 35771118
-
Protective effect of the roots extract of Platycodon grandiflorum on bile duct ligation-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013 Nov;32(11):1197-205. doi: 10.1177/0960327112474832. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23424213
-
Effects of Yinchenhao decoction on self-regulation of renin-angiotensin system by targeting angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in bile duct-ligated rat liver.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2015 Aug;35(4):519-524. doi: 10.1007/s11596-015-1463-9. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26223920
References
-
- Riordan SM, Williams R. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:473–9. - PubMed
-
- Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, Blei AT. Hepatic encephalopathy—definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology. 2002;35:716–21. - PubMed
-
- Mousseau D, Baker G, Butterworth R. Increased density of catalytic sites and expression of brain monoamine oxidase A in humans with hepatic encephalopathy. J Neurochem. 1997;68:1200–8. - PubMed
-
- Yurdaydin C, Karavelioǧlu D, Onaran O, Çelik T, Yaşa MH, Uzunalimoǧlu Ö. Opioid receptor ligands in human hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol. 1998;29:796–801. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
