Biosynthesis of plant tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids through an imine reductase route
- PMID: 32190259
- PMCID: PMC7067268
- DOI: 10.1039/c9sc03773j
Biosynthesis of plant tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids through an imine reductase route
Abstract
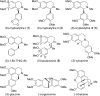
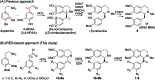
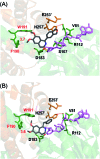
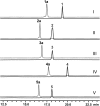
Herein, we report a biocatalytic approach to synthesize plant tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids (THIQAs) from dihydroisoquinoline (DHIQ) precursors using imine reductases and N-methyltransferase (NMT). The imine reductase IR45 was engineered to significantly expand its substrate specificity, enabling efficient and stereoselective conversion of 1-phenyl and 1-benzyl 6,7-dimethoxy-DHIQs into the corresponding (S)-tetrahydroisoquinolines (S-THIQs). Coclaurine N-methyltransferase (CNMT) was able to further efficiently convert these (S)-THIQ intermediates into (S)-THIQAs. By assembling IRED, CNMT, and glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) in one reaction, we effectively constituted two artificial biosynthetic pathways in Escherichia coli and successfully applied them to the production of five (S)-THIQAs. This highly efficient (100% yield from DHIQs) and easily tailorable (adding other genes) biosynthetic approach will be useful for producing a variety of plant THIQAs.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020.
Figures

References
-
- Liu W., Liu S., Jin R., Guo H., Zhao J. Org. Chem. Front. 2015;2:288–299.
- Chrzanowska M., Grajewska A., Rozwadowska M. D. Chem. Rev. 2016;116:12369–12465. - PubMed
-
- Perez M., Wu Z., Scalone M., Ayad T., Ratovelomanana-Vidal V. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015:6503–6514.
- Singh I. P., Shah P. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017;27:17–36. - PubMed
-
- Narcross L., Fossati E., Bourgeois L., Dueber J. E., Martin V. J. J. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34:228–241. - PubMed
-
- Stadler R., Kutchan T. M., Zenk M. H. Phytochemistry. 1989;28:1083–1086.
- De-Eknamkul W., Suttipanta N., Kutchan T. M. Phytochemistry. 2000;55:177–181. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

