Network-based identification of signature genes KLF6 and SPOCK1 associated with oral submucous fibrosis
- PMID: 32190310
- PMCID: PMC7058035
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2020.1991
Network-based identification of signature genes KLF6 and SPOCK1 associated with oral submucous fibrosis
Abstract
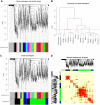
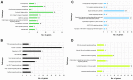
The molecular mechanism of oral submucous fibrosis (OSF) is yet to be fully elucidated. The identification of reliable signature genes to screen patients with a high risk of OSF and to provide oral cancer surveillance is therefore required. The present study produced a filtering criterion based on network characteristics and principal component analysis, and identified the genes that were involved in OSF prognosis. Two gene expression datasets were analyzed using meta-analysis, the results of which revealed 1,176 biologically significant genes. A co-expression network was subsequently constructed and weighted gene modules were detected. The pathway and functional enrichment analyses of the present study allowed for the identification of modules 1 and 2, and their respective genes, SPARC (osteonectin), cwcv and kazal like domain proteoglycan 1 (SPOCK1) and kruppel like factor 6 (KLF6), which were involved in the occurrence of OSF. The results revealed that both genes had a prominent role in epithelial to mesenchymal transition during OSF progression. The genes identified in the present study require further exploration and validation within clinical settings to determine their roles in OSF.
Keywords: eigengene; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; meta-analysis; module; protein-protein interaction; singular value decomposition; weighted gene co-expression network analysis.
Copyright: © Singh et al.
Figures




References
-
- Ekanayaka RP, Tilakaratne WM. Oral submucous fibrosis: Review on mechanisms of pathogenesis and malignant transformation. J Carcinog Mutagen, 2013. Available from: https://www.omicsonline.org/oral-submucous-fibrosis-a-clinico-histopatho.... - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
