Single-institution Retrospective Analysis of Prognostic Factors Influencing Very Late-onset Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder
- PMID: 32190467
- PMCID: PMC7061783
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.6912
Single-institution Retrospective Analysis of Prognostic Factors Influencing Very Late-onset Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder
Abstract
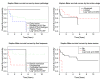
Background Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is a rare complication following transplant (solid organ or allogeneic) due to the proliferation of lymphoid cells in the immunosuppressed state. The incidence of PTLD follows a bimodal distribution, with high incidence immediately after transplant (early-onset PTLD), followed by a decline and then a high-incidence again five years after transplantation (late-onset PTLD). This study exclusively aims to identify prognostic factors for the subgroup of PTLD, described as very late-onset PTLD, occurring after 10 years of transplant. Methods This study was conducted at the University of Florida, with the requisite study population identified through the cancer registry. Data were collected by individual chart review and analyzed. Survival estimates and univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to measure the effects of each variable on overall survival. Results A total of 33 patients were identified, with a median age at transplant of 42.3 years, while the median age at PTLD diagnosis was 54.7 years. Median time from transplant to PTLD diagnosis was 13.3 years. Kidney (30.3%), liver (27.3%), and heart (24.2%) transplants were the most common allografts associated with very late PTLD development. The most common pathology was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in 45.5% of patients. CHOP+/-R (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride (hydroxydaunorubicin), vincristine sulfate (Oncovin), prednisone, rituximab) was the most common chemo regimen used as the initial choice in 36.4% of patients. Median survival was 5.4 years. Univariate analysis showed that age at diagnosis over 65, male gender, bone marrow involvement, past medical history (PMH) of malignancy, immunosuppression regimen at PTLD diagnosis, and initial and final best response to treatment were statistically significant (p <0.05) factors associated with survival. On multivariate analysis, bone marrow involvement was significantly associated with poor survival (p=0.008). Surprisingly, performance status, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) status, pathology type, Ann-Arbor stage, and chemotherapy regimen were not significantly associated with survival. At the end of the study, 48.5% of patients achieved complete remission and the allograft survived in 84.8%. Conclusions In this retrospective study of very-late onset PTLD, we identified factors associated with survival different from early and late PTLD. These factors should be considered during the treatment of this subgroup of PTLD patients.
Keywords: ebv ptld; late-onset ptld; post transplant lymphoproliferative disorder; prognostic factors for ptld; very late-onset ptld.
Copyright © 2020, Bishnoi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- De novo cancer-related death in Australian liver and cardiothoracic transplant recipients. Na R, Grulich AE, Meagher NS, McCaughan GW, Keogh AM, Vajdic CM. Am J Transplant. 2013;13:1296–1304. - PubMed
-
- Identifying the patient at risk for post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Cockfield SM. Transpl Infect Dis. 2001;3:70–78. - PubMed
-
- Risk of lymphoproliferative disorders after bone marrow transplantation: a multi-institutional study. Curtis RE, Travis LB, Rowlings PA, et al. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10498590. Blood. 1999;94:2208–2216. - PubMed
-
- Epidemiology of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders in adult kidney and kidney pancreas recipients: report of the French registry and analysis of subgroups of lymphomas. Caillard S, Lamy FX, Quelen C, et al. Am J Transplant. 2012;12:682–693. - PubMed
-
- Incidence of PTLD in pediatric renal transplant recipients receiving basiliximab, calcineurin inhibitor, sirolimus and steroids. McDonald RA, Smith JM, Ho M, et al. Am J Transplant. 2008;8:984–989. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous