Real world study for the concordance between IBM Watson for Oncology and clinical practice in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients at a lung cancer center in China
- PMID: 32191394
- PMCID: PMC7180560
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.13391
Real world study for the concordance between IBM Watson for Oncology and clinical practice in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients at a lung cancer center in China
Abstract
Background: IBM Watson for Oncology (WFO) provides physicians with evidence-based treatment options. This study was designed to explore the concordance of the suggested therapeutic regimen for advanced non-small cell lung (NSCLC) cancer patients between the updated version of WFO and physicians in our department, in order to reflect the differences of cancer treatment between China and the United States.
Methods: Retrospective data from 165 patients with advanced NSCLC from September 2014 to March 2018 were entered manually into WFO. WFO recommendations were provided in three categories: recommended, for consideration, and not recommended. Concordance was analyzed by comparing the treatment decisions proposed by WFO with the real treatment. Potential influenced factors were also analyzed.
Results: Overall, the treatment recommendations were concordant in 73.3% (121/165) of cases. When two alternative drugs such as icotinib and nedaplatin were included as "for consideration," the total consistency could be elevated from 73.3% to 90.3%(149/165). The logistic regression analysis showed that gender (P = 0.096), ECOG (P = 0.0.502), smoking (P = 0.455), and pathology (P = 0.633) had no effect on consistency, but stages (P = 0.019), including stage ≤III (77.8%, 21/27) and stage IV (93.5%, 129/138) had significant effects on consistency.
Conclusions: In China, most of the treatment recommendations of WFO are consistent with the real world treatment. Factors such as patient preferences, prices, drug approval and medical insurance are also taken into consideration, and they ultimately affect the inconsistency. To be comprehensively and rapidly applied in China, localization needs to be accelerated by WFO.
Keywords: Advanced disease; Watson for Oncology; artificial intelligence; concordance; non-small cell lung cancer.
© 2020 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Non‐small cell lung cancer (Version 5.2019). [Cited 10 Sep 2019.] Available from URL: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/nscl.pdf.
-
- IBM (US) . IBM Watson Health ‐ IBM Watson for Oncology [Internet]. IBM Corporation, New York; 2019. [Cited 19 Feb 2020.] Available from URL: https://www.ibm.com/downloads/cas/AONROW12.
-
- Somashekhar SP, Sepulveda MJ, Puglielli S et al Watson for Oncology and breast cancer treatment recommendations: Agreement with an expert multidisciplinary tumor board. Ann Oncol 2018; 29: 418–23. - PubMed
-
- Baek JH, Ahn S‐M, Urman A et al Use of a cognitive computing system for treatment of colon and gastric cancer in Korea. J Clin Oncol 2017; 35: e18204.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

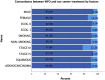
 ) inconsistency and (
) inconsistency and ( ) consistency.
) consistency.