Policy Changes and Child Blood Lead Levels by Age 2 Years for Children Born in Illinois, 2001-2014
- PMID: 32191520
- PMCID: PMC7144441
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2020.305566
Policy Changes and Child Blood Lead Levels by Age 2 Years for Children Born in Illinois, 2001-2014
Abstract
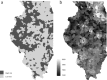
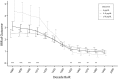
Objectives. To evaluate how lowering the blood lead level (BLL) intervention threshold affects childhood lead testing policy.Methods. We geocoded 4.19 million Illinois lead testing records (2001-2016) and linked to 2.37 million birth records (2001-2014), data on housing age, industrial emissions, and roads. We used multinomial logistic regression to determine predictors of BLLs of 10 micrograms per deciliter (µg/dL) or greater, 5 to 9 µg/dL, and 4 µg/dL.Results. We found that 2.2% of children had BLLs of 10 µg/dL or greater, 8.9% had BLLs of 5 to 9 µg/dL, and 5.7% had BLLs of 4 µg/dL. Pre-1930 housing was associated with more than 2- to 4-fold increased relative risk of BLLs above all thresholds. Housing built in 1951 to 1978 was associated with increased relative risk of BLLs of 5 to 9 µg/dL (relative risk ratio [RRR] = 1.14; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.06, 1.21) but not with increased relative risk of BLLs of 10 µg/dL or greater (RRR = 0.99; 95% CI = 0.84, 1.16). At a given address, previous BLLs of 5 to 9 µg/dL or BLLs of 10 µg/dL or greater were associated with increased risk of BLLs of 5 to 9 µg/dL or BLLs of 10 µg/dL or greater among current occupants by 2.37- (95% CI = 2.20, 2.54) fold and 4.08- (95% CI = 3.69, 4.52) fold, respectively.Conclusions. The relative importance of determinants of above-threshold BLLs changes with decreasing intervention thresholds.Public Health Implications. States may need to update lead screening guidelines when decreasing the intervention threshold.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood lead levels and associated sociodemographic factors among preschool children in the South Eastern region of China.Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2012 Jan;26(1):61-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3016.2011.01234.x. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2012. PMID: 22150709 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of blood lead levels >or= 5 micro g/dL among US children 1 to 5 years of age and socioeconomic and demographic factors associated with blood of lead levels 5 to 10 micro g/dL, Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1994.Pediatrics. 2003 Dec;112(6 Pt 1):1308-13. doi: 10.1542/peds.112.6.1308. Pediatrics. 2003. PMID: 14654602
-
Surveillance for elevated blood lead levels among children--United States, 1997-2001.MMWR Surveill Summ. 2003 Sep 12;52(10):1-21. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2003. PMID: 14532866
-
Effects of Blood Lead Levels <10 µg/dL in School-Age Children and Adolescents: A Scoping Review.Pediatrics. 2024 Oct 1;154(Suppl 2):e2024067808F. doi: 10.1542/peds.2024-067808F. Pediatrics. 2024. PMID: 39352036
-
Blood lead levels in children, China.Environ Res. 2006 Jul;101(3):412-8. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2005.11.007. Epub 2006 Jan 25. Environ Res. 2006. PMID: 16442092 Review.
Cited by
-
Methods in Public Health Environmental Justice Research: a Scoping Review from 2018 to 2021.Curr Environ Health Rep. 2023 Sep;10(3):312-336. doi: 10.1007/s40572-023-00406-7. Epub 2023 Aug 15. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2023. PMID: 37581863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferrie JP, Rolf K, Troesken W. Lead exposure and the perpetuation of low socioeconomic status. 2015. Available at: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/56f8/7f0d51c12c0772c53eec2bd70b6d000b51.... Accessed February 10, 2020.
-
- Reyes JW. Lead policy and academic performance: insights from Massachusetts. Harv Educ Rev. 2015;85(1):75–108.
-
- Aizer A, Currie J. Lead and juvenile delinquency: new evidence from linked birth, school, and juvenile detention records. Rev Econ Stat. 2019;101(4):575–587.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

