Aminoglycoside use and intensive care unit-acquired weakness: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32191708
- PMCID: PMC7082020
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230181
Aminoglycoside use and intensive care unit-acquired weakness: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The relationship between aminoglycoside use and intensive care unit (ICU)-acquired weakness remains controversial. In the present study, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to examine the relationship between aminoglycoside use and ICU-acquired weakness in critically ill patients.
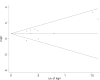
Methods: The PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials and Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature databases were searched from the earliest available date to July 10, 2019. Randomized controlled trials and prospective cohort studies examining the relationship between aminoglycosides and ICU-acquired weakness in adult ICU patients were included. Two authors independently screened titles/abstracts, reviewed full text and extracted data from the included studies. We performed the Meta-analysis using Stata version 15.0 and used the DerSimonian-Laird random effects model for data analyses. Heterogeneity was evaluated using the χ2 statistic and I2 statistic. Publication bias was evaluated with funnel plots qualitatively, the Begg's test and Egger's test quantitatively.
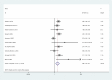
Results: Ten prospective cohort studies were included and analysed in this review. The overall effect sizes of the studies revealed a statistically significant relationship between aminoglycoside use and ICU-acquired weakness (OR, 2.06; 95%CI, 1.33-3.21; I2 = 56%). Subgroup and sensitivity analyses suggested a significant association between aminoglycoside use and studies limited to patients with clinical weakness (OR, 2.74; 95%CI, 1.83-4.10; I2 = 0%), and not to studies limited to patients with abnormal electrophysiology (OR, 1.78; 95%CI, 0.94-3.39; I2 = 59%), a large sample size (OR, 1.81; 95%CI, 0.97-3.39; I2 = 75%), or low risk of bias (OR, 1.59; 95%CI, 0.97-2.60; I2 = 56%); however, statistical heterogeneity was obvious. There were no significant publication biases found in the review.
Conclusions: The review revealed a significant relationship between aminoglycoside use and ICU-acquired weakness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
References
-
- Hermans G, Van Mechelen H, Clerckx B, Vanhullebusch T, Mesotten D, Wilmer A, et al. Acute outcomes and 1-year mortality of intensive care unit-acquired weakness. A cohort study and propensity-matched analysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014; 190(4): 410–420. 10.1164/rccm.201312-2257OC . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sharshar T, Bastuji-Garin S, Stevens RD, Durand MC, Malissin I, Rodriguez P, et al. Presence and severity of intensive care unit-acquired paresis at time of awakening are associated with increased intensive care unit and hospital mortality. Critical care medicine. 2009; 37(12): 3047–3053. 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181b027e9 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources