The Critical Role of miRNAs in Regulation of Flowering Time and Flower Development
- PMID: 32192095
- PMCID: PMC7140873
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11030319
The Critical Role of miRNAs in Regulation of Flowering Time and Flower Development
Abstract
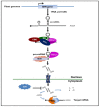
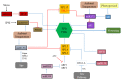
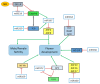
Flowering is an important biological process for plants that ensures reproductive success. The onset of flowering needs to be coordinated with an appropriate time of year, which requires tight control of gene expression acting in concert to form a regulatory network. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are non-coding RNAs known as master modulators of gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Many different miRNA families are involved in flowering-related processes such as the induction of floral competence, floral patterning, and the development of floral organs. This review highlights the diverse roles of miRNAs in controlling the flowering process and flower development, in combination with potential biotechnological applications for miRNAs implicated in flower regulation.
Keywords: floral induction; flower development; flower regulation; juvenility; microRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Floral induction and flower formation--the role and potential applications of miRNAs.Plant Biotechnol J. 2015 Apr;13(3):282-92. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12340. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Plant Biotechnol J. 2015. PMID: 25641615 Review.
-
Evolutionary conservation of microRNA regulatory programs in plant flower development.Dev Biol. 2013 Aug 15;380(2):133-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.05.009. Epub 2013 May 21. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23707900 Review.
-
To bloom or not to bloom: role of microRNAs in plant flowering.Mol Plant. 2015 Mar;8(3):359-77. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.018. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Mol Plant. 2015. PMID: 25737467 Review.
-
Characterization and comparative profiling of the small RNA transcriptomes in two phases of flowering in Cymbidium ensifolium.BMC Genomics. 2015 Aug 20;16(1):622. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1764-1. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26289943 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs having strong positive interaction with mRNAs reveal their regulatory nature during flowering in a wild relative of pigeonpea (Cajanus scarabaeoides).Mol Biol Rep. 2020 May;47(5):3305-3317. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05400-y. Epub 2020 Apr 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32248382
Cited by
-
The Pivotal Role of Noncoding RNAs in Flowering Time Regulation.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 23;14(12):2114. doi: 10.3390/genes14122114. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional verification of the JmLFY gene associated with the flowering of Juglans mandshurica Maxim.PeerJ. 2023 Mar 7;11:e14938. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14938. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36908820 Free PMC article.
-
The Characters of Non-Coding RNAs and Their Biological Roles in Plant Development and Abiotic Stress Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 8;23(8):4124. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084124. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Novel microRNAs Involved in the Continuous Flowering Trait of Longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 8;23(24):15565. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415565. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555206 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis, Mode of Action and the Interactions of Plant Non-Coding RNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 26;24(13):10664. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310664. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

