A Retrospective on eIF2A-and Not the Alpha Subunit of eIF2
- PMID: 32192132
- PMCID: PMC7139343
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21062054
A Retrospective on eIF2A-and Not the Alpha Subunit of eIF2
Abstract
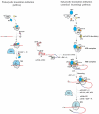
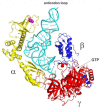
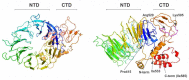
Initiation of protein synthesis in eukaryotes is a complex process requiring more than 12 different initiation factors, comprising over 30 polypeptide chains. The functions of many of these factors have been established in great detail; however, the precise role of some of them and their mechanism of action is still not well understood. Eukaryotic initiation factor 2A (eIF2A) is a single chain 65 kDa protein that was initially believed to serve as the functional homologue of prokaryotic IF2, since eIF2A and IF2 catalyze biochemically similar reactions, i.e., they stimulate initiator Met-tRNAi binding to the small ribosomal subunit. However, subsequent identification of a heterotrimeric 126 kDa factor, eIF2 (α,β,γ) showed that this factor, and not eIF2A, was primarily responsible for the binding of Met-tRNAi to 40S subunit in eukaryotes. It was found however, that eIF2A can promote recruitment of Met-tRNAi to 40S/mRNA complexes under conditions of inhibition of eIF2 activity (eIF2α-phosphorylation), or its absence. eIF2A does not function in major steps in the initiation process, but is suggested to act at some minor/alternative initiation events such as re-initiation, internal initiation, or non-AUG initiation, important for translational control of specific mRNAs. This review summarizes our current understanding of the eIF2A structure and function.
Keywords: alternative initiation; eIF2A; non-AUG initiation; stress response; translational initiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Yeast eIF2A has a minimal role in translation initiation and uORF-mediated translational control in vivo.Elife. 2024 Jan 24;12:RP92916. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92916. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38266075 Free PMC article.
-
An mRNA-specific tRNAi carrier eIF2A plays a pivotal role in cell proliferation under stress conditions: stress-resistant translation of c-Src mRNA is mediated by eIF2A.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 9;45(1):296-310. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1117. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27899592 Free PMC article.
-
eIF2A, an initiator tRNA carrier refractory to eIF2α kinases, functions synergistically with eIF5B.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Dec;75(23):4287-4300. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2870-4. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30019215 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999 Jan;31(1):25-9. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(98)00128-9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10216940 Review.
-
Hepatitis C Virus Translation Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 27;21(7):2328. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072328. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32230899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing the Power of Purple Sweet Potato Color and Myo-Inositol to Treat Classic Galactosemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 4;23(15):8654. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158654. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955788 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-Based Markers of Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Buccal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systems Biology Approach.Biochem Res Int. 2023 Apr 24;2023:5512894. doi: 10.1155/2023/5512894. eCollection 2023. Biochem Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37143570 Free PMC article.
-
A chiral fluorescent Ir(iii) complex that targets the GPX4 and ErbB pathways to induce cellular ferroptosis.Chem Sci. 2023 Jan 9;14(5):1114-1122. doi: 10.1039/d2sc06171f. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 36756328 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Translation Factors EIF2S1, EIF5A and EIF6 in Intestinal-Type Adenocarcinoma (ITAC).Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 11;13(22):5649. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225649. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830804 Free PMC article.
-
Increased levels of eIF2A inhibit translation by sequestering 40S ribosomal subunits.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Oct 13;51(18):9983-10000. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad683. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37602404 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

