Modulation of Cellular Biochemistry, Epigenetics and Metabolomics by Ketone Bodies. Implications of the Ketogenic Diet in the Physiology of the Organism and Pathological States
- PMID: 32192146
- PMCID: PMC7146425
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12030788
Modulation of Cellular Biochemistry, Epigenetics and Metabolomics by Ketone Bodies. Implications of the Ketogenic Diet in the Physiology of the Organism and Pathological States
Abstract
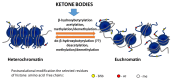
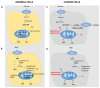
Ketone bodies (KBs), comprising β-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetone, are a set of fuel molecules serving as an alternative energy source to glucose. KBs are mainly produced by the liver from fatty acids during periods of fasting, and prolonged or intense physical activity. In diabetes, mainly type-1, ketoacidosis is the pathological response to glucose malabsorption. Endogenous production of ketone bodies is promoted by consumption of a ketogenic diet (KD), a diet virtually devoid of carbohydrates. Despite its recently widespread use, the systemic impact of KD is only partially understood, and ranges from physiologically beneficial outcomes in particular circumstances to potentially harmful effects. Here, we firstly review ketone body metabolism and molecular signaling, to then link the understanding of ketone bodies' biochemistry to controversies regarding their putative or proven medical benefits. We overview the physiological consequences of ketone bodies' consumption, focusing on (i) KB-induced histone post-translational modifications, particularly β-hydroxybutyrylation and acetylation, which appears to be the core epigenetic mechanisms of activity of β-hydroxybutyrate to modulate inflammation; (ii) inflammatory responses to a KD; (iii) proven benefits of the KD in the context of neuronal disease and cancer; and (iv) consequences of the KD's application on cardiovascular health and on physical performance.
Keywords: cancer; epigenetics; inflammatory response; ketogenic diet; ketone bodies; β-hydroxybutyrate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Henderson C.B., Filloux F.M., Alder S.C., Lyon J.L., Caplin D.A. Efficacy of the Ketogenic Diet as a Treatment Option for Epilepsy: Meta-Analysis. J. Child. Neurol. 2006;21:193–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

