Unusual accumulation of a wide array of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms in a patient with cytomegalovirus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a case report
- PMID: 32192451
- PMCID: PMC7083060
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-020-04966-z
Unusual accumulation of a wide array of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms in a patient with cytomegalovirus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a case report
Abstract
Background: Infections with multidrug-resistant organisms (MDRO) pose a serious threat to patients with dysregulated immunity such as in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), but such infections have rarely been comprehensively characterized. Here, we present a fatal case of HLH secondary to cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection complicated by both anti-viral drug resistance and sepsis from multiple MDROs including pandrug-resistant superbug bacteria.
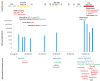
Case presentation: A previously healthy, six-year-old boy presented with a 45-day history of fever prior to a diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and hemorrhagic colitis, both associated with CMV. On hospital admission, the patient was found to be colonized with multiple, multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria including vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and carbapenamase-producing organisms (CPO). He eventually developed respiratory, urine and bloodstream infections with highly drug-resistant, including pandrug-resistant bacteria, which could not be controlled by antibiotic treatment. Antiviral therapy also failed to contain his CMV infection and the patient succumbed to overwhelming bacterial and viral infection. Whole genome sequencing (WGS) of the MDR bacteria and metagenomic analysis of his blood sample revealed an unusual accumulation of a wide range of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms in a single patient, including antiviral resistance to ganciclovir, and resistance mechanisms to all currently available antibiotics.
Conclusions: The case highlights both the risk of acquiring MDR superbugs and the severity of these infections in HLH patients.
Keywords: Antiviral resistance; Cytomegalovirus; Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; Multidrug-resistant organism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Successful treatment of cytomegalovirus-induced hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with ruxolitinib as a first-line treatment.Infect Dis Now. 2021 May;51(3):311-313. doi: 10.1016/j.idnow.2020.10.010. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Infect Dis Now. 2021. PMID: 33934812 No abstract available.
-
Pregnancy-related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis associated with cytomegalovirus infection: A diagnostic and therapeutic challenge.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Aug;54(4):432-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2014.11.023. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2015. PMID: 26384065 Review.
-
Cytomegalovirus reactivation in a critically ill patient: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2018 Jun 11;12(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s13256-018-1681-4. J Med Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29886847 Free PMC article.
-
A case of hemophagocytic syndrome in a patient with fulminant ulcerative colitis superinfected by cytomegalovirus.Korean J Intern Med. 2013 May;28(3):352-5. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2013.28.3.352. Epub 2013 May 1. Korean J Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23682230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secondary haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by postnatally acquired cytomegalovirus infection in a late preterm infant.Infection. 2017 Jun;45(3):355-359. doi: 10.1007/s15010-016-0970-3. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Infection. 2017. PMID: 28093696
Cited by
-
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis presented with fever of unknown origin: A case study and literature review.Clin Case Rep. 2021 Mar 8;9(4):2350-2355. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.4033. eCollection 2021 Apr. Clin Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33936693 Free PMC article.
-
Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis Caused by Mycobacterium abscessus in Children-A Case Report.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020 Nov 27;8(1):ofaa579. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa579. eCollection 2021 Jan. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33447640 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid evidence assessment exploring whether antimicrobial resistance complicates non-infectious health conditions and healthcare services, 2010-20.JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2021 Nov 15;3(4):dlab171. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlab171. eCollection 2021 Dec. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2021. PMID: 34806009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Narrative Review of Healthcare-Associated Gram-Negative Infections Among Pediatric Patients in Middle Eastern Countries.Infect Dis Ther. 2023 May;12(5):1217-1235. doi: 10.1007/s40121-023-00799-w. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Infect Dis Ther. 2023. PMID: 37071349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Status of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Fungi in the Arabian Peninsula.Biology (Basel). 2021 Nov 6;10(11):1144. doi: 10.3390/biology10111144. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827138 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Review on Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling drug-resistant infections globally. https://amr-review.org/home.html. Accessed 26 June 2019.
-
- Pulmonary infections in immunocompromised patients. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pulmonary-infections-in-immunocompromi.... Accessed 26 June 2019.
-
- Fürstberger A, Maucher M, Kestler HA. Extended pairwise local alignment of wild card DNA/RNA sequences using dynamic programming. J Stat Comput Simul. 2013;85(1):3–13. doi: 10.1080/00949655.2014.928294. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

