Factors Influencing Variability in the Performance of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Detecting Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review
- PMID: 32192942
- PMCID: PMC8942295
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euo.2020.02.005
Factors Influencing Variability in the Performance of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Detecting Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
Context: There is a lack of comprehensive data regarding the factors that influence the diagnostic accuracy of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) to detect and localize clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa).
Objective: To systematically review the current literature assessing the factors influencing the variability of mpMRI performance in csPCa diagnosis.
Evidence acquisition: A computerized bibliographic search of Medline/PubMed database was performed for all studies assessing magnetic field strength, use of an endorectal coil, assessment system used by radiologists and inter-reader variability, experience of radiologists and urologists, use of a contrast agent, and use of computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) tools in relation to mpMRI diagnostic accuracy.
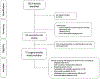
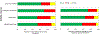
Evidence synthesis: A total of 77 articles were included. Both radiologists' reading experience and urologists'/radiologists' biopsy experience were the main factors that influenced diagnostic accuracy. Therefore, it is mandatory to indicate the experience of the interpreting radiologists and biopsy-performing urologists to support the reliability of the findings. The most recent Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) guidelines are recommended for use as the main assessment system for csPCa, given the simplified and standardized approach as well as its particular added value for less experienced radiologists. Biparametric MRI had similar accuracy to mpMRI; however, biparametric MRI performed better with experienced readers. The limited data available suggest that the combination of CAD and radiologist readings may influence diagnostic accuracy positively.
Conclusions: Multiple factors affect the accuracy of mpMRI and MRI-targeted biopsy to detect and localize csPCa. The high heterogeneity across the studies underlines the need to define the experience of radiologists and urologists, implement quality control, and adhere to the most recent PI-RADS assessment guidelines. Further research is needed to clarify which factors impact the accuracy of the MRI pathway and how.
Patient summary: We systematically reported the factors influencing the accuracy of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa). These factors are significantly related to each other, with the experience of the radiologists being the dominating factor. In order to deliver the benefits of mpMRI to diagnose csPCa, it is necessary to develop expertise for both radiologists and urologists, implement quality control, and adhere to the most recent Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System assessment guidelines.
Keywords: Diagnosis, Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging; Magnetic resonance imaging; Prostate cancer; Targeted biopsy.
Copyright © 2020 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Stabile A, Giganti F, Rosenkrantz AB, et al. Multiparametric MRI for prostate cancer diagnosis: current status and future directions. Nat Rev Urol 2020;17:41–61. - PubMed
-
- Giganti F, Rosenkrantz AB, Panebianco V, et al. The evolution of MRI of the prostate: the past, the present, and the future. Am J Roentgenol 2019;213:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Woo S, Suh CH, Eastham JA, et al. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging-stratified clinical pathways and systematic transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy pathway for the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur Urol Oncol 2019;2:605–16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kasivisvanathan V, Stabile A, Neves JB, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging-targeted biopsy versus systematic biopsy in the detection of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol 2019;76:284–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

