Serpina3c Regulates Adipogenesis by Modulating Insulin Growth Factor 1 and Integrin Signaling
- PMID: 32193145
- PMCID: PMC7076559
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.100961
Serpina3c Regulates Adipogenesis by Modulating Insulin Growth Factor 1 and Integrin Signaling
Abstract
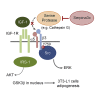
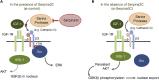
Preadipocyte differentiation can be induced upon a hormonal treatment, and various factors secreted by the cells may contribute to adipogenesis. In this study, RNA-seq revealed Serpina3c as a critical factor regulating the signaling network during adipogenesis. Serpina3c is a secretory protein and is highly expressed in fat tissues. Knockdown of Serpina3c decreased adipogenesis by attenuating the mitotic clonal expansion of 3T3-L1 cells. These cells exhibited decreases in integrin α5, which abolished the phosphorylation of integrin β3. We found that Serpina3c inhibits a serine protease that regulates integrin α5 degradation. Knockdown of Serpina3c disrupted integrin-mediated insulin growth factor 1 (IGF-1) signaling and ERK activation. Serpina3c-mediated regulation of integrin-IGF-1 signaling is also associated with AKT activation, which affects the nuclear translocation of GSK3β. Altogether, our results indicate that Serpina3c secreted from differentiating adipocytes inhibits serine proteases to modulate integrin/IGF-1-mediated ERK and AKT signaling and thus is a critical factor contributing to adipogenesis.
Keywords: Developmental Biology; Molecular Biology; Transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Barrett A.J., Rawlings N.D., O'Brien E.A. The MEROPS database as a protease information system. J. Struct. Biol. 2001;134:95–102. - PubMed
-
- Cowan K.J., Law D.A., Phillips D.R. Identification of Shc as the primary protein binding to the tyrosine-phosphorylated beta(3) subunit of alpha(IIb)beta(3) during outside-in integrin platelet signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:36423–36429. - PubMed
-
- Fagerholm S.C., Hilden T.J., Gahmberg C.G. P marks the spot: site-specific integrin phosphorylation regulates molecular interactions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004;29:504–512. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

