Multi-modular AI Approach to Streamline Autism Diagnosis in Young Children
- PMID: 32193406
- PMCID: PMC7081341
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-61213-w
Multi-modular AI Approach to Streamline Autism Diagnosis in Young Children
Abstract
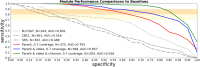
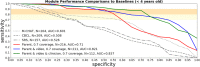
Autism has become a pressing healthcare challenge. The instruments used to aid diagnosis are time and labor expensive and require trained clinicians to administer, leading to long wait times for at-risk children. We present a multi-modular, machine learning-based assessment of autism comprising three complementary modules for a unified outcome of diagnostic-grade reliability: A 4-minute, parent-report questionnaire delivered via a mobile app, a list of key behaviors identified from 2-minute, semi-structured home videos of children, and a 2-minute questionnaire presented to the clinician at the time of clinical assessment. We demonstrate the assessment reliability in a blinded, multi-site clinical study on children 18-72 months of age (n = 375) in the United States. It outperforms baseline screeners administered to children by 0.35 (90% CI: 0.26 to 0.43) in AUC and 0.69 (90% CI: 0.58 to 0.81) in specificity when operating at 90% sensitivity. Compared to the baseline screeners evaluated on children less than 48 months of age, our assessment outperforms the most accurate by 0.18 (90% CI: 0.08 to 0.29 at 90%) in AUC and 0.30 (90% CI: 0.11 to 0.50) in specificity when operating at 90% sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are affiliated with Cognoa Inc. in an employment and/or advisory capacity.
Figures

References
-
- Association., A. P. & Association., A. P. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders : DSM-5 (American Psychiatric Association Arlington, VA, 2013), 5th ed. edn.
-
- Dawson, G. et al. Randomized, controlled trial of an intervention for toddlers with autism: The early start denver model. Pediatrics125, e17–e23 10.1542/peds.2009-0958, http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/125/1/e17.full.pdf (2010). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

