Chest CT manifestations of new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a pictorial review
- PMID: 32193638
- PMCID: PMC7088323
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-06801-0
Chest CT manifestations of new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a pictorial review
Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak, first reported in Wuhan, China, has rapidly swept around the world just within a month, causing global public health emergency. In diagnosis, chest computed tomography (CT) manifestations can supplement parts of limitations of real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay. Based on a comprehensive literature review and the experience in the frontline, we aim to review the typical and relatively atypical CT manifestations with representative COVID-19 cases at our hospital, and hope to strengthen the recognition of these features with radiologists and help them make a quick and accurate diagnosis.Key Points• Ground glass opacities, consolidation, reticular pattern, and crazy paving pattern are typical CT manifestations of COVID-19.• Emerging atypical CT manifestations, including airway changes, pleural changes, fibrosis, nodules, etc., were demonstrated in COVID-19 patients.• CT manifestations may associate with the progression and prognosis of COVID-19.
Keywords: Coronavirus infections; Pneumonia; Tomography, X-ray computed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures
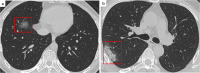
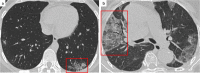
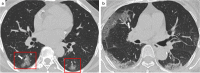
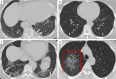
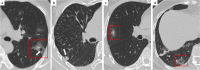
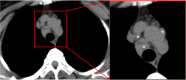
Comment in
-
Mobile X-rays are highly valuable for critically ill COVID patients.Eur Radiol. 2020 Sep;30(9):5217-5219. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06918-2. Epub 2020 May 13. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32405750 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Development and validation of COVID-19 Radiological Risk Score (COVID-RRS): a multivariable radiological score to estimate the in-hospital mortality risk in COVID-19 patients.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Jan;27(1):384-394. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202301_30892. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36647887
References
-
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W et al (2020) A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
-
- World Health Organization (2020) Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report–39. World Health Organization, Geneva. Available via https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed 3 Mar 2020
-
- World Health Organization (2020) Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report–42. World Health Organization, Geneva. Available via https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/20200302-sitrep-42-.... Accessed 3 Mar 2020
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

