A CT-based radiomics nomogram for prediction of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status in patients with gastric cancer
- PMID: 32194306
- PMCID: PMC7072015
- DOI: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2020.01.08
A CT-based radiomics nomogram for prediction of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status in patients with gastric cancer
Abstract
Objective: To develop and validate a computed tomography (CT)-based radiomics nomogram for predicting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status in patients with gastric cancer.
Methods: This retrospective study included 134 patients with gastric cancer (HER2-negative: n=87; HER2-positive: n=47) from April 2013 to March 2018, who were then randomly divided into training (n=94) and validation (n=40) cohorts. Radiomics features were obtained from the CT images showing gastric cancer. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression analysis was utilized for building the radiomics signature. A multivariable logistic regression method was applied to develop a prediction model incorporating the radiomics signature and independent clinicopathologic risk predictors, which were then visualized as a radiomics nomogram. The predictive performance of the nomogram was assessed in the training and validation cohorts.
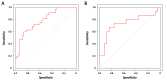
Results: The radiomics signature was significantly associated with HER2 status in both training (P<0.001) and validation (P=0.023) cohorts. The prediction model that incorporated the radiomics signature and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level demonstrated good discriminative performance for HER2 status prediction, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.799 [95% confidence interval (95% CI): 0.704-0.894] in the training cohort and 0.771 (95% CI: 0.607-0.934) in the validation cohort. The calibration curve of the radiomics nomogram also showed good calibration. Decision curve analysis showed that the radiomics nomogram was useful.
Conclusions: We built and validated a radiomics nomogram with good performance for HER2 status prediction in gastric cancer. This radiomics nomogram could serve as a non-invasive tool to predict HER2 status and guide clinical treatment.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; X ray; computed tomography; human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; radiomics.
Copyright © 2020 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Value of Predicting Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Status in Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagogastric Junction on CT-Based Radiomics Nomogram.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 14;11:707686. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.707686. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34722254 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative prediction for lauren type of gastric cancer: A radiomics nomogram analysis based on CT images and clinical features.J Xray Sci Technol. 2021;29(4):675-686. doi: 10.3233/XST-210888. J Xray Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 34024809 Clinical Trial.
-
Development and Validation of a Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2016 Jun 20;34(18):2157-64. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.9128. Epub 2016 May 2. J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27138577
-
18F-FDG PET/CT-based radiomics nomogram for the preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 8;12:911168. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.911168. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36003788 Free PMC article.
-
Application of radiomics in precision prediction of diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer.Jpn J Radiol. 2023 Mar;41(3):245-257. doi: 10.1007/s11604-022-01352-4. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Jpn J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36260211 Review.
Cited by
-
Accurate preoperative staging and HER2 status prediction of gastric cancer by the deep learning system based on enhanced computed tomography.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 14;12:950185. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.950185. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36452488 Free PMC article.
-
A virtual biopsy study of microsatellite instability in gastric cancer based on deep learning radiomics.Insights Imaging. 2023 Jun 7;14(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01438-1. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37286810 Free PMC article.
-
CT-based radiomic nomogram for preoperative prediction of DNA mismatch repair deficiency in gastric cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 16;12:883109. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.883109. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36185292 Free PMC article.
-
From Images to Genes: Radiogenomics Based on Artificial Intelligence to Achieve Non-Invasive Precision Medicine in Cancer Patients.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jan;12(2):e2408069. doi: 10.1002/advs.202408069. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39535476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preoperative 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics analysis for predicting HER2 expression and prognosis in gastric cancer.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Mar 1;13(3):1537-1549. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-148. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 36915308 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
World Health Organization. World Cancer Report 2014. 150 cours Albert Thomas, 69372. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2014.
-
-
-
Ajani JA, D’Amico TA . NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology-Gastric Cancer (Version 2. 2019): National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 2019.
-
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
