Study of the cwaRS-ldcA Operon Coding a Two-Component System and a Putative L,D-Carboxypeptidase in Lactobacillus paracasei
- PMID: 32194510
- PMCID: PMC7062640
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00156
Study of the cwaRS-ldcA Operon Coding a Two-Component System and a Putative L,D-Carboxypeptidase in Lactobacillus paracasei
Abstract
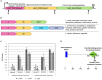
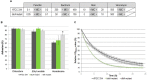
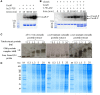
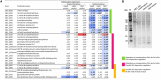
The cell surface is the primary recognition site between the bacterium and the host. An operon of three genes, LSEI_0219 (cwaR), LSEI_0220 (cwaS), and LSEI_0221 (ldcA), has been previously identified as required for the establishment of Lactobacillus paracasei in the gut. The genes cwaR and cwaS encode a predicted two-component system (TCS) and ldcA a predicted D-alanyl-D-alanine carboxypeptidase which is a peptidoglycan (PG) biosynthesis enzyme. We explored the functionality and the physiological role of these three genes, particularly their impact on the bacterial cell wall architecture and on the bacterial adaptation to environmental perturbations in the gut. The functionality of CwaS/R proteins as a TCS has been demonstrated by biochemical analysis. It is involved in the transcriptional regulation of several genes of the PG biosynthesis. Analysis of the muropeptides of PG in mutants allowed us to re-annotate LSEI_0221 as a putative L,D-carboxypeptidase (LdcA). The absence of this protein coincided with a decrease of two surface antigens: LSEI_0020, corresponding to p40 or msp2 whose implication in the host epithelial homeostasis has been recently studied, and LSEI_2029 which has never been functionally characterized. The inactivation of each of these three genes induces susceptibility to antimicrobial peptides (hBD1, hBD2, and CCL20), which could be the main cause of the gut establishment deficiency. Thus, this operon is necessary for the presence of two surface antigens and for a suitable cell wall architecture.
Keywords: antimicrobial peptides; carboxypeptidase; gene regulation; host–microbe interaction; lactic acid bacteria; peptidoglycan; two-component system.
Copyright © 2020 Scornec, Palud, Pédron, Wheeler, Petitgonnet, Boneca, Cavin, Sansonetti and Licandro.
Figures


References
-
- Abo-Amer A. E., Munn J., Jackson K., Aktas M., Golby P., Kelly D. J., et al. (2004). DNA interaction and phosphotransfer of the C4-dicarboxylate-responsive DcuS-DcuR two-component regulatory system from Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 186 1879–1889. 10.1128/jb.186.6.1879-1889.2004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

