miRNA-Coordinated Schizophrenia Risk Network Cross-Talk With Cardiovascular Repair and Opposed Gliomagenesis
- PMID: 32194626
- PMCID: PMC7064629
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00149
miRNA-Coordinated Schizophrenia Risk Network Cross-Talk With Cardiovascular Repair and Opposed Gliomagenesis
Abstract
Background: Schizophrenia risk genes are widely investigated, but a systemic analysis of miRNAs contributing to schizophrenia is lacking.
Methods: Schizophrenia-associated genetic loci profiles were derived from a genome-wide association study (GWAS) from the Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (PGC) dataset. Experimentally confirmed relationships between miRNAs and their target genes were retrieved from a miRTarBase. A competitive gene set association analysis for miRNA-target regulations was conducted by the Multi-marker Analysis of GenoMic Annotation (MAGMA) and further validated by literature-based functional pathway analysis using Pathway Studio. The association between the targets of three miRNAs and schizophrenia was further validated using a GWAS of antipsychotic treatment responses.
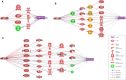
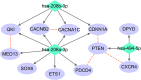
Results: Three novel schizophrenia-risk miRNAs, namely, miR-208b-3p, miR-208a-3p, and miR-494-5p, and their targetomes converged on calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 C (CACNA1C) and B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2), and these are well-known contributors to schizophrenia. Both miR-208a-3p and miR-208b-3p reduced the expression of the RNA-binding protein Quaking (QKI), whose suppression commonly contributes to demyelination of the neurons and to ischemia/reperfusion injury. On the other hand, both QKI and hsa-miR-494-5p were involved in gliomagenesis.
Conclusion: Presented results point at an orchestrating role of miRNAs in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. The sharing of regulatory networks between schizophrenia and other pathologies may explain higher cardiovascular mortality and lower odds of glioma previously reported in psychiatric patients.
Keywords: gliomagenesis; heart disease; miR-208a-3p; miR-208b-3p; miR-494-5p; miRNA; quaking; schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2020 Cao, Baranova, Yue, Yu, Zhu, Zhang and Liu.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

