Circulating MicroRNAs in Plasma Decrease in Response to Sarcopenia in the Elderly
- PMID: 32194634
- PMCID: PMC7066121
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00167
Circulating MicroRNAs in Plasma Decrease in Response to Sarcopenia in the Elderly
Abstract
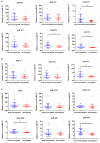
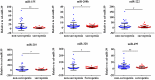
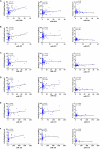
sarcopenia has been defined as the aging-related disease with the declined mass, strength, and function of skeletal muscle, which is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in elders. Current diagnostic criteria of sarcopenia have not been agreed internationally, and the clinical diagnostic biomarkers for sarcopenia have not been identified. Circulating miRNAs (miRNAs, miRs) have recently been characterized as novel biomarkers for sarcopenia. However, the change of circulating miRNAs in response to sarcopenia are still not fully understood. Here, we enrolled a total of 93 elderly patients clinically diagnosed with sarcopenia and matching 93 non-sarcopenia elderly in this study. Specifically, levels of candidate circulating miRNAs which were involved in angiogenesis, inflammation and enriched in muscle and/or cardiac tissues were detected in these two groups. In small-sample screening experiments, plasma miR-155, miR-208b, miR-222, miR-210, miR-328, and miR-499 levels were significantly down-regulated in sarcopenia compared to those who non-sarcopenia. In contrast, miR-1, mir-133a, miR-133b, miR-21, miR-146a, miR-126, miR-221, and miR-20a were not changed significantly. Subsequently, we expanded the sample size to further detection and verification, and found that plasma miR-155, miR-208b, miR-222, miR-210, miR-328, and miR-499 levels in the sarcopenia group were significantly reduced compared to the non-sarcoma group, which is consistent with the results of the small-sample screening experiment. In addition, we showed that ASM/Height2, handgrip strength, knee extension and 4-meter velocity in sarcopenia group were significantly lower than those in non-sarcopenia group. Here we correlated the decrease of miR-208b, miR-499, miR-155, miR-222, miR-328, and miR-210 in sarcopenia group and non-sarcopenia group with diagnostic indexes of sarcopenia (ASM/Height2, Handgrip strength and 4-meter velocity) after adjusting sex. The results showed that miR-208b and miR-155 changes were significantly correlated with handgrip strength in woman, miR-208b, miR-499, and miR-222 changes were significantly correlated with ASM/Height2 in man, while other miRNAs changes did not show a strong correlation with these diagnostic indexes. In conclusion, plasma miR-208b, miR-499, miR-155, miR-222, miR-328, and miR-210 decrease in response to sarcopenia in the elderly. Although further studies are needed to clarify the potential use of circulating miRNAs as biomarkers of sarcopenia, present findings set the stage for defining circulating miRNAs as biomarkers and suggesting their physiological roles in elderly with sarcopenia.
Keywords: biomarker; circulating microRNAs; elderly; plasma; sarcopenia.
Copyright © 2020 He, Zhang, Zhang, Feng, Zheng, Wang, Zhang, Guo and Ye.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increasing Fracture Risk Associates With Plasma Circulating MicroRNAs in Aging People's Sarcopenia.Front Physiol. 2021 Jun 7;12:678610. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.678610. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34163374 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating MicroRNA-486 and MicroRNA-146a serve as potential biomarkers of sarcopenia in the older adults.BMC Geriatr. 2021 Jan 30;21(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02040-0. BMC Geriatr. 2021. PMID: 33516190 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miR-29b decrease in response to sarcopenia in patients with cardiovascular risk factors in older Chinese.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Dec 20;9:1094388. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1094388. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36606278 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of plasma miRNAs, muscle miRNAs and mitochondrial miRNAs in the pathophysiology of frailty.Exp Gerontol. 2019 Sep;124:110637. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2019.110637. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Exp Gerontol. 2019. PMID: 31199979 Review.
-
The Roles of myomiRs in the Pathogenesis of Sarcopenia: From Literature to In Silico Analysis.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 1. doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01373-0. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40025274 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma microRNA signature associated with skeletal muscle wasting in post-menopausal osteoporotic women.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024 Apr;15(2):690-701. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13421. Epub 2024 Jan 25. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024. PMID: 38272849 Free PMC article.
-
Association of circulating hsa-miRNAs with sarcopenia: the SarcoPhAge study.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024 Mar 14;36(1):70. doi: 10.1007/s40520-024-02711-z. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024. PMID: 38485856 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-1-mediated miR-let-7g-5p triggers interlukin-6 and TNF-α to cause myopathy and chronic adipose inflammation in elderly patients with diabetes mellitus.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Apr 25;14(8):3633-3651. doi: 10.18632/aging.204034. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35468098 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Criteria and Measurement Techniques of Sarcopenia: A Critical Evaluation of the Up-to-Date Evidence.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 1;16(3):436. doi: 10.3390/nu16030436. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38337720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutrition and microRNAs: Novel Insights to Fight Sarcopenia.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Oct 2;9(10):951. doi: 10.3390/antiox9100951. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33023202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

