Genetic Divergence and Relationship Among Opisthopappus Species Identified by Development of EST-SSR Markers
- PMID: 32194635
- PMCID: PMC7065708
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00177
Genetic Divergence and Relationship Among Opisthopappus Species Identified by Development of EST-SSR Markers
Abstract
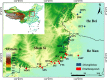
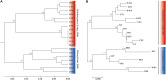
Opisthopappus Shih is an endemic and endangered genus restricted to the Taihang Mountains that has important ornamental and economic value. According to the Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae (FRPS, Chinese version), this genus contains two species (Opisthopappus longilobus and Opisthopappus taihangensis), whereas in the Flora of China (English version) only one species O. taihangensis is present. The interspecific phylogenetic relationship remains unclear and undefined, which might primarily be due to the lack of specific molecular markers for phylogenetic analysis. For this study, 2644 expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeats (EST-SSRs) from 33,974 unigenes using a de novo transcript assembly of Opisthopappus were identified with a distribution frequency of 7.78% total unigenes. Thereinto, mononucleotides (1200, 45.39%) were the dominant repeat motif, followed by trinucleotides (992, 37.52%), and dinucleotides (410, 15.51%). The most dominant trinucleotide repeat motif was ACC/GGT (207, 20.87%). Based on the identified EST-SSRs, 245 among 1444 designed EST-SSR primers were selected for the development of potential molecular markers. Among these markers, 63 pairs of primers (25.71%) generated clear and reproducible bands with expected sizes. Eventually, 11 primer pairs successfully amplified all individuals from the studied populations. Through the EST-SSR markers, a high level of genetic diversity was detected between Opisthopappus populations. A significant genetic differentiation between the O. longilobus and O. taihangensis populations was found. All studied populations were divided into two clusters by UPGMA, NJ, STRUCTURE, and PCoA. These results fully supported the view of the FRPS, namely, that O. longilobus and O. taihangensis should be regarded as two distinct species. Our study demonstrated that transcriptome sequences, as a valuable tool for the quick and cost-effective development of molecular markers, was helpful toward obtaining comprehensive EST-SSR markers that could contribute to an in-depth assessment of the genetic and phylogenetic relationships between Opisthopappus species.
Keywords: EST-SSRs development; Opisthopappus; phylogenetic relationship; population genetics; transcriptome sequencing.
Copyright © 2020 Chai, Ye, Wang, Zhou, Wu, Gao, Han, Zang, Zhang, Ru, Sun and Wang.
Figures



References
-
- Annadurai R. S., Neethiraj R., Jayakumar V., Damodaran A. C., Rao S. N., Katta M. A., et al. (2013). De Novo transcriptome assembly (NGS) of Curcuma longa L. rhizome reveals novel transcripts related to anticancer and antimalarial terpenoids. PLoS One 8:e56217. 10.1371/journal.pone.0056217 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asp T., Frei U. K., Didion T., Nielsen K. K., Lübberstedt T. (2007). Frequency, type, and distribution of EST-SSRs from three genotypes of Lolium perenne, and their conservation across orthologous sequences of Festuca arundinacea, Brachypodium distachyon, and Oryza sativa. BMC Plant Biol. 7:36. 10.1186/1471-2229-7-36 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bazzo B. R., de Carvalho L. M., Carazzolle M. F., Pereira G. A. G., Colombo C. A. (2018). Development of novel EST-SSR markers in the macaúba palm (Acrocomia aculeata) using transcriptome sequencing and cross-species transferability in Arecaceae species. BMC Plant Biol. 18:276. 10.1186/s12870-018-1509-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

