Role of HSP27 in the multidrug sensitivity and resistance of colon cancer cells
- PMID: 32194698
- PMCID: PMC7039054
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.11255
Role of HSP27 in the multidrug sensitivity and resistance of colon cancer cells
Abstract
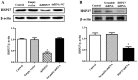
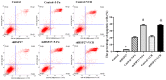
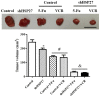
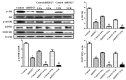
Multidrug resistance in cancer cells is a primary factor affecting therapeutic efficacy. Heat shock 27 kD protein 1 (HSP27) is associated with cell apoptosis and resistance to chemotherapy. However, the mechanisms underlying HSP27-associated pathways in colon cancer cells remain unclear. Therefore, the present study used short hairpin (sh) RNA to inhibit HSP27 expression in colon cancer cells in order to investigate the effects in vitro and in vivo. Flow cytometry was used to investigate cell apoptosis and a xenograft model was employed to examine the tumorigenesis. Protein expression was measured by Western blotting. The results revealed that suppression of HSP27 expression significantly increased cell apoptosis, inhibited tumor growth and enhanced sensitivity to the anti-cancer agents 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and vincristine (VCR). shHSP27 significantly decreased the expression of notch receptor 1 and the phosphorylation level of Akt and mTOR, and enhanced the effect of 5-FU and VCR. In conclusion, HSP27 suppression enhanced the sensitivity of colon cancer cells to 5-FU and VCR, and increased colon cancer cell apoptosis with and without chemotherapy. Therefore, the development of novel therapeutic agents that inhibit the expression of HSP27 may offer a new treatment option for colon cancer.
Keywords: colon cancer; heat shock 27 kD protein 1; multidrug sensitivity; notch receptor 1-Akt-mTOR pathway.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppression of heat shock protein 27 expression promotes 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in colon cancer cells in a xenograft model.Oncol Rep. 2012 Oct;28(4):1269-74. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1935. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22842517
-
Heat shock protein 27 knockdown using nucleotide‑based therapies enhances sensitivity to 5-FU chemotherapy in SW480 human colon cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2018 Mar;39(3):1119-1124. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6180. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29328475
-
MiR-214 sensitizes human colon cancer cells to 5-FU by targeting Hsp27.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019 Mar 14;24:22. doi: 10.1186/s11658-019-0143-3. eCollection 2019. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30915129 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of HSP27 increases the anti‑tumor effects of quercetin in human leukemia U937 cells.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jan;13(1):689-96. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4600. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 26648539 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Hsp27 in Chemotherapy Resistance.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 14;10(4):897. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040897. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The prognostic importance of the negative regulators of ferroptosis, GPX4 and HSPB1, in patients with colorectal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2025 Jan 15;29(3):144. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.14890. eCollection 2025 Mar. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 39850719 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of phosphorylated HSP27 on the proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its mechanism].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Nov;38(11):1017-1023. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.11.005. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39534892 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Methoxybenzamide derivative of nimesulide from anti-fever to anti-cancer: Chemical characterization and cytotoxicity.Saudi Pharm J. 2022 May;30(5):485-493. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.03.004. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Saudi Pharm J. 2022. PMID: 35693435 Free PMC article.
-
Heat Shock Proteins, a Double-Edged Sword: Significance in Cancer Progression, Chemotherapy Resistance and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 14;16(8):1500. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081500. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unfolded protein response during the progression of colorectal carcinogenesis.Acta Cir Bras. 2025 Jan 13;40:e400725. doi: 10.1590/acb400725. eCollection 2025. Acta Cir Bras. 2025. PMID: 39813534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gill S, Loprinzi CL, Sargent DJ, Thomé SD, Alberts SR, Haller DG, Benedetti J, Francini G, Shepherd LE, Francois Seitz J, et al. Pooled analysis of fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy for stage II and III colon cancer: Who benefits and by how much? J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1797–1806. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.09.059. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Meyerhardt JA. Adjuvant therapy for stage II and III colon cancer. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2010;8:772–774. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
