Development and validation of a 4-gene combination for the prognostication in lung adenocarcinoma patients
- PMID: 32194805
- PMCID: PMC7052877
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.37003
Development and validation of a 4-gene combination for the prognostication in lung adenocarcinoma patients
Abstract
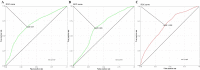
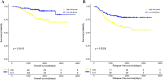
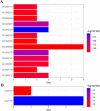
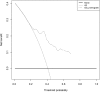
Objective: To identify a multi-gene prognostic factor in patients with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Materials and methods Prognosis-related genes were screened in the TCGA-LUAD cohort. Then, patients in this cohort were randomly separated into training set and test set. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was performed to the penalized the Cox proportional hazards regression (CPH) model on the training set, and a prognostication combination based on the result of LASSO analysis was developed. By performing Kaplan-Meier curve analysis, univariate and multivariable CPH model on the overall survival (OS) as well as recurrence free survival (RFS), the prognostication performance of the multigene combination were evaluated. Moreover, we constructed a nomogram and performed decision curve analysis to evaluate the clinical application of the multigene combination. Results We obtained 99 prognosis-related genes and screened out a 4-gene combination (including CIDEC, ZFP3, DKK1, and USP4) according to the LASSO analysis. The results of survival analyses suggested that patients in the 4-gene combination low-risk group had better OS and RFS than those in the 4-gene combination high-risk group. The 4-gene mentioned was demonstrated to be independent prognostic factor of patients with LUAD in the training set(OS, HR=11.962, P<0.001; RFS, HR=9.281, P<0.001) and test set (OS, HR=5.377, P=0.003; RFS, HR=2.949, P=0.104). More importantly, its prognosis performance was well in the validation set (OS, HR=0.955, P=0.002; RFS, HR=1.042, P<0.001). Conclusions We introduced a 4-gene combination which could predict the survival of LUAD patients and might be an independent prognostic factor in LUAD.
Keywords: least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; lung adenocarcinoma; prognostication; survival analysis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A large cohort study identifying a novel prognosis prediction model for lung adenocarcinoma through machine learning strategies.BMC Cancer. 2019 Sep 5;19(1):886. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6101-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31488089 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation profiling to predict recurrence risk in stage Ι lung adenocarcinoma: Development and validation of a nomogram to clinical management.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jul;24(13):7576-7589. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15393. Epub 2020 Jun 12. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32530136 Free PMC article.
-
A seven-gene prognostic signature predicts overall survival of patients with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Jun 6;21(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01975-z. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34092242 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a prognostic model for lung adenocarcinoma based on bioinformatics analysis of metabolic genes.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 May;9(5):3518-3538. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-1571. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117717 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a novel prognostic signature of microRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma.PeerJ. 2021 Jan 8;9:e10470. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10470. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33510968 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
To Develop and Validate the Combination of RNA Methylation Regulators for the Prognosis of Patients with Gastric Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Oct 23;13:10785-10795. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S276239. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33122917 Free PMC article.
-
m6A-Related Genes Contribute to Poor Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Oct 26;2022:2427987. doi: 10.1155/2022/2427987. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 36339682 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Stool Methylation Test for the Non-Invasive Screening of Gastric and Colorectal Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 28;12:860701. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.860701. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35419280 Free PMC article.
-
Signature identification of relapse-related overall survival of early lung adenocarcinoma after radical surgery.PeerJ. 2021 Aug 5;9:e11923. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11923. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34430085 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a three-long noncoding RNA signature for predicting prognosis of patients with gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Nov 28;26(44):6929-6944. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i44.6929. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33311941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Mao Y, Yang D, He J, Krasna MJ. Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016;25:439–45. - PubMed
-
- Bunn PA Jr. Worldwide overview of the current status of lung cancer diagnosis and treatment. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136:1478–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

