Fugan Wan alleviates hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting ACE/Ang II/AT-1R signaling pathway and enhancing ACE2/Ang 1-7/Mas signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis rat models
- PMID: 32194907
- PMCID: PMC7061829
Fugan Wan alleviates hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting ACE/Ang II/AT-1R signaling pathway and enhancing ACE2/Ang 1-7/Mas signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis rat models
Abstract
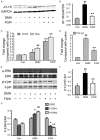
Hepatic fibrosis is a repair and healing reaction for chronic injuries of liver. This study aimed to investigate protective effects of Fugan Wan (FGW) on hepatic fibrosis and clarify associated mechanisms. Hepatic fibrosis model was established by administrating dimethyl nitrosamine (DMN) to rats. Rats were divided into control, DMN and FGW groups. Haematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining was conducted to evaluate inflammatory response in hepatic fibrosis tissues. Sirius red staining was used to assess collagen disposition. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was employed to detect antiotensin-converting enzyme homologue 2 (ACE2), Mas, transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) mRNA. Western blot was used to examine collagen I, smooth muscle actin α (α-SMA), angiotensin type 1 receptor (AT-1R), extra-cellular regulated protein kinase (ERK), phosphorylated ERK (p-ERK), c-Jun and phosphorylated-c-Jun (p-c-Jun) expression. The results indicated that FGW significantly reduced inflammatory response of hepatic fibrosis tissues. FGW significantly decreased collagen deposition compared to that of DMN group (P < 0.01). FGW significantly down-regulated α-SMA expression compared to that of DMN group (P < 0.01). FGW significantly decreased AT-1R levels compared to that of DMN group (P < 0.01). Comparing with DMN group, ACE2 and Mas mRNA levels were significantly increased in FGW group (P < 0.01). FGW significantly down-regulated p-c-Jun and p-ERK1/2 compared to DMN group (P < 0.01). GFW significantly inhibited compared to DMN group (P < 0.01). In conclusion, FGW alleviated hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting ACE/Ang II/AT-1R signaling and enhancing ACE2/Ang 1-7/Mas signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis rat models.
Keywords: Fugan Wan; hepatic fibrosis; renin angiotensin system; signaling pathway.
AJTR Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
