The functions and properties of cullin-5, a potential therapeutic target for cancers
- PMID: 32194910
- PMCID: PMC7061844
The functions and properties of cullin-5, a potential therapeutic target for cancers
Abstract
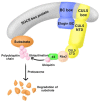
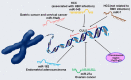
Cullin-5 (CUL5), a scaffold protein in active cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase (CRL) complexes, is a member of the cullin family of proteins. The CUL5-type ubiquitin ligase can target multiple proteins involved in ubiquitination and proteasome degradation. CUL5 plays positive roles in regulating cell growth, proliferation and physiological and other processes in the human body. It has been found that the expression of CUL5 is significantly downregulated in various cancer cells, which affects the course of the cancers. Here, we reviewed the current data on the expression and role of CUL5 in both normal and cancer cells, its possible mechanisms, and its potential as a therapeutic target for cancers.
Keywords: Cullin-5; cancer; microRNAs; regulation; therapeutics; ubiquitin.
AJTR Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Lamsoul I, Uttenweiler-Joseph S, Moog-Lutz C, Lutz PG. Cullin 5-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases, new therapeutic targets? Biochimie. 2016;122:339–347. - PubMed
-
- Li Q, Cui M, Yang F, Li N, Jiang B, Yu Z, Zhang D, Wang Y, Zhu X, Hu H, Li PS, Ning SL, Wang S, Qi H, Song H, He D, Lin A, Zhang J, Liu F, Zhao J, Gao L, Yi F, Xue T, Sun JP, Gong Y, Yu X. A cullin 4B-RING E3 ligase complex fine-tunes pancreatic delta cell paracrine interactions. J Clin Invest. 2017;127:2631–2646. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burnatowska-Hledin MA, Spielman WS, Smith WL, Shi P, Meyer JM, Dewitt DL. Expression cloning of an AVP-activated, calcium-mobilizing receptor from rabbit kidney medulla. Am J Physiol. 1995;268:F1198–1210. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
