Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 affects the invasion and apoptosis of renal cell carcinoma by regulating the miR-363-3p-Twist1 interaction
- PMID: 32194916
- PMCID: PMC7061841
Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 affects the invasion and apoptosis of renal cell carcinoma by regulating the miR-363-3p-Twist1 interaction
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 affects the invasion and apoptosis of renal cell carcinoma by regulating the miR-363-3p-Twist1 interaction.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Dec 15;15(12):7035-7036. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38186991 Free PMC article.
Abstract
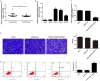
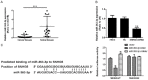
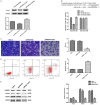
Non-coding RNA dysregulation is associated with many human diseases, including cancer. This study explored the effects of lncRNA SNHG5 on clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). We found that lncRNA SNHG5 is upregulated in human ccRCC tissues and that lncRNA SNHG5 inhibition reduced ccRCC cell invasion and promoted apoptosis in vitro. Bioinformatics database searching revealed that lncRNA SNHG5 is predicted to regulate the interaction between miR-363-3p and Twist1. We further verified a ccRCC biomarker panel, which consists of lncRNA SNHG5, miR-363-3p, and Twist1 in ccRCC tissue samples. The direct SNHG5-miR-363-3p and Twist1-miR-363-3p interactions were confirmed via dual-luciferase reporter assays. Additionally, functional assays demonstrated that SNHG5 promotes cell invasion and inhibits apoptosis, while miR-363-3p inhibits cell invasion and promotes apoptosis via an interaction with Twist1. Furthermore, we found that Twist1 promotes tumor metastasis by regulating matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)2 and MMP9 levels. Together, these results suggest that lncRNA SNHG5 may predict ccRCC patient clinical outcome and serve as a novel anti-ccRCC therapeutic target.
Keywords: Twist1; ccRCC; lncRNA SNHG5; metastasis; miR-363-3p.
AJTR Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
lncRNA SNHG5 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma by sponging miR-655-3p/FZD4 axis.Oncol Lett. 2020 Dec;20(6):310. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12173. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 33093919 Free PMC article.
-
The lncRNA SNHG5-mediated miR-205-5p downregulation contributes to the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by targeting ZEB1.Cancer Med. 2020 Jun;9(12):4251-4264. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3052. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Cancer Med. 2020. Retraction in: Cancer Med. 2023 Feb;12(4):5172. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5090. PMID: 32281285 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
miR-93-3p inhibition suppresses clear cell renal cell carcinoma proliferation, metastasis and invasion.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 24;8(47):82824-82834. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20458. eCollection 2017 Oct 10. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29137305 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA SNHG5 affects cell proliferation, metastasis and migration of colorectal cancer through regulating miR-132-3p/CREB5.Cancer Biol Ther. 2019;20(4):524-536. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1537579. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30395767 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates E2F1 expression by competitively sponging endogenous miR-29a-3p in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Cell Biosci. 2017 Dec 1;7:65. doi: 10.1186/s13578-017-0193-z. eCollection 2017. Cell Biosci. 2017. PMID: 29214011 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Long Noncoding RNA Small Nucleolar Host Gene: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Urological Cancers.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 22;11:638721. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.638721. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33968736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA SLC2A1-AS1 induced by GLI3 promotes aerobic glycolysis and progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by sponging miR-378a-3p to enhance Glut1 expression.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Sep 13;40(1):287. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02081-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. Retraction in: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Mar 9;42(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02632-1. PMID: 34517880 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A review on the role of long non-coding RNA and microRNA network in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its tumor microenvironment.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Feb 2;23(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02861-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 36732762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNA-363 during tumor progression and invasion.J Physiol Biochem. 2024 Aug;80(3):481-499. doi: 10.1007/s13105-024-01022-1. Epub 2024 May 1. J Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38691273 Review.
-
Advances in pathogenesis of preeclampsia.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024 May;309(5):1815-1823. doi: 10.1007/s00404-024-07393-6. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024. PMID: 38421424
References
-
- Ljungberg B, Campbell SC, Choi HY, Cho HY, Jacqmin D, Lee JE, Weikert S, Kiemeney LA. The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2011;60:615–621. - PubMed
-
- Bex A, Jonasch E, Kirkali Z, Mejean A, Mulders P, Oudard S, Patard JJ, Powles T, Van Poppel H, Wood CG. Integrating surgery with targeted therapies for renal cell carcinoma: Current evidence and ongoing trials. Eur Urol. 2010;58:819–828. - PubMed
-
- Liz J, Portela A, Soler M, Gómez A, Ling H, Michlewski G, Calin GA, Guil S, Esteller M. Regulation of pri-miRNA processing by a long noncoding RNA transcribed from an ultraconserved region. Mol Cell. 2014;55:138–147. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
