Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Could Be Effective Against Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Brain Metastases Harboring Uncommon EGFR Mutations
- PMID: 32195178
- PMCID: PMC7066117
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00224
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Could Be Effective Against Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Brain Metastases Harboring Uncommon EGFR Mutations
Abstract
Background: The significance of uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and brain metastasis (BM) remains unclear. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) liquid biopsy is a novel tool for assessing EGFR mutations in BM. This study aimed to evaluate the EGFR mutations in patients with NSCLC and newly diagnosed BM and to examine the effect of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) on BM harboring CSF-tested uncommon EGFR mutations. Methods: This was a prospective study of 21 patients with NSCLC and BM diagnosed between 04/2018 and 01/2019. CSF was obtained to detect the BM EGFR mutations by next-generation sequencing. BM characteristics at magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and EGFR-TKI response were examined. Results: Of 21 patients with NSCLC, 10 (47.6%) had leptomeningeal metastasis (LM), while 11 (52.4%) had brain parenchymal metastasis (BPM); 13 (61.9%) had confirmed EGFR mutation-positive primary tumors. The uncommon mutation rate in CSF ctDNA was 33.3% (7/21). Among those with EGFR mutation-positive primary tumors, the rate of uncommon EGFR mutations in CSF was 53.8% (7/13). Uncommon EGFR mutations were more common in patients with LM than in patients with PBM (6/11, 54.5% vs. 1/10, 10%), and included G719A, L861Q, L703P, and G575R. TKI was effective for four patients with BMs harboring uncommon EGFR mutations. Conclusion: In patients with NSCLC and LM, the rate of uncommon EGFR mutation was high. The BMs with uncommon EGFR mutations seem to respond to EGFR-TKI treatment. CSF liquid biopsy could reveal the EGFR genetic profile of the BM and help guide treatment using small-molecule TKI.
Keywords: brain metastasis; epidermal growth factor receptor; mutation; non-small cell lung cancer; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Copyright © 2020 Ma, Zhang, Tang, Ye, Li, Mu, Li, Liu, Xiang, Huang and Jiang.
Figures


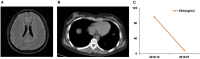
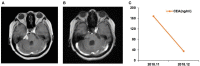
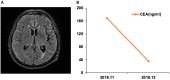
Similar articles
-
Cerebrospinal fluid ctDNA testing shows an advantage over plasma ctDNA testing in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 10;13:1322635. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1322635. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38269023 Free PMC article.
-
Two non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with brain metastasis harboring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) G719X and L861Q mutations benefited from aumolertinib: two cases report and review of the literature.Heliyon. 2022 Aug 28;8(9):e10407. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10407. eCollection 2022 Sep. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36119883 Free PMC article.
-
Uncommon mutation types of epidermal growth factor receptor and response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;80(6):1179-1187. doi: 10.1007/s00280-017-3464-9. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29063948
-
Next-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in epidermal growth factor receptor -mutant non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2016 Mar;93:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.01.003. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Lung Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26898616 Review.
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exceptional response to afatinib in a patient with persistent G719A EGFR-mutant NSCLC.Lung Cancer Manag. 2022 Apr 21;11(1):LMT54. doi: 10.2217/lmt-2021-0001. eCollection 2022 Mar. Lung Cancer Manag. 2022. PMID: 35463918 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic comparison between cerebrospinal fluid and primary tumor revealed the genetic events associated with brain metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 12;12(10):935. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04223-4. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34642306 Free PMC article.
-
A Lung Cancer Patient Harboring a Rare Oncogenic EGFR Exon 20 V786M Mutation Responded to a Third-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor: Case Report and Review of the Literature.Front Oncol. 2022 May 18;12:912426. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.912426. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35664749 Free PMC article.
-
Overview on Therapeutic Options in Uncommon EGFR Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): New Lights for an Unmet Medical Need.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 17;24(10):8878. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108878. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical outcomes of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring distinct subtypes of EGFR mutations and receiving first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors: brain metastasis and de novo T790M matters.BMC Cancer. 2022 Feb 21;22(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09245-5. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35189835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Preusser M, Winkler F, Valiente M, Manegold C, Moyal E, Widhalm G, et al. . Recent advances in the biology and treatment of brain metastases of non-small cell lung cancer: summary of a multidisciplinary roundtable discussion. ESMO Open. (2018) 3:e000262. 10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000262 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

