Diagnostic Accuracy of Droplet Digital PCR and Amplification Refractory Mutation System PCR for Detecting EGFR Mutation in Cell-Free DNA of Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 32195189
- PMCID: PMC7063461
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00290
Diagnostic Accuracy of Droplet Digital PCR and Amplification Refractory Mutation System PCR for Detecting EGFR Mutation in Cell-Free DNA of Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
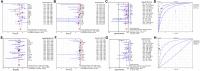
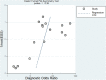
Background: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation testing in plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from advanced lung cancer patients is an emerging clinical tool. This meta-analysis was designed to determine the diagnostic accuracy of two common PCR systems, droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) and amplification refractory mutation system PCR (ARMS-PCR), for detecting EGFR mutation in cfDNA. Materials and methods: A systematic search was carried out based on PubMed, Web of science, Embase and the Cochrane library. Data from eligible studies were extracted and pooled to calculate the sensitivity, specificity, diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), area under the summary receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUROC), using tissue biopsy results as the standard method. Subgroup analyses were performed regarding EGFR mutation type, tumor stage, and EGFR-TKI treatment. Results: Twenty-five studies involving 4,881 cases were included. The plasma testing sensitivity, specificity, DOR, and AUROC, compared with the matched tumor tissues, were 72.1%, 95.6%, 38.5, 0.89 for ddPCR, and 65.3%, 98.2%, 52.8, 0.71 for ARMS-PCR, respectively, through indirect comparison, significant differences were found in sensitivity (P = 0.003) and specificity (P = 0.007). Furthermore, significant difference was found in sensitivity between tumor stage subgroups (IIIB-IV subgroup vs. IA-IV subgroup) in ARMS-PCR (73.7 vs. 64.2%, P = 0.008), but not in ddPCR (72.5 vs. 71.2%, P = 0.756). Conclusions: This study demonstrates that ddPCR and ARMS-PCR have a high specificity with a practical sensitivity for detecting EGFR mutation in cfDNA, which supports their application as a supplement or a conditional-alternative to tissue biopsy in clinical practice for genotyping. It seems that ddPCR has a higher sensitivity than ARMS-PCR, especially in early stages.
Keywords: amplification refractory mutation system PCR (ARMS-PCR); cell free DNA (cfDNA); droplet digital PCR (ddPCR); epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); lung cancer.
Copyright © 2020 Li, He, Liang, Cheng, Li, Xiong, Zhao, Guo, Liu, He and Liang.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Clinical Value of Droplet Digital PCR and Super-ARMS Detection of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutation in Plasma Circulating Tumor DNA of Patients with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2020 Feb 20;23(2):84-90. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.02.03. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32093452 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Multiplex picoliter-droplet digital PCR for quantitative assessment of EGFR mutations in circulating cell-free DNA derived from advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Aug;16(2):1157-1166. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6712. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 29067441 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the SuperARMS and Droplet Digital PCR for Detecting EGFR Mutation in ctDNA From NSCLC Patients.Transl Oncol. 2018 Apr;11(2):542-545. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.02.007. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29525631 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy of droplet digital PCR for the detection of EGFR mutation (T790M) in plasma: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Apr;503:190-196. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.11.023. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 31805270
-
The diagnostic accuracy of digital PCR, ARMS and NGS for detecting KRAS mutation in cell-free DNA of patients with colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 26;16(3):e0248775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248775. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33770081 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Copy Number Variation and Rearrangements Assessment in Cancer: Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR with the Current Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 29;22(9):4732. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094732. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33946969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analytical and clinical validation of a custom 15-gene next-generation sequencing panel for the evaluation of circulating tumor DNA mutations in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 18;17(10):e0276161. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276161. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36256645 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of different platforms in detecting EGFR mutations using cerebrospinal fluid cell-free DNA from non-small-cell lung cancer patients with leptomeningeal metastases.Thorac Cancer. 2023 May;14(14):1251-1259. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14866. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36977550 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Cell-Free DNA Genotyping: From an Emerging Concept to a Standard-of-Care Tool in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Oncologist. 2021 Oct;26(10):e1812-e1821. doi: 10.1002/onco.13889. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Oncologist. 2021. PMID: 34216176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of First-Generation EGFR-TKIs Combined with Chemotherapy for Treatment-Naïve Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Harboring Sensitive EGFR Mutations: A Single-Center, Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase II Clinical Trial.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Jun 16;14:2557-2567. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S313056. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34168480 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, et al. . Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2012) 13:239–46. 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

