Moderate Fluid Shear Stress Regulates Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression to Promote Autophagy and ECM Homeostasis in the Nucleus Pulposus Cells
- PMID: 32195253
- PMCID: PMC7064043
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00127
Moderate Fluid Shear Stress Regulates Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression to Promote Autophagy and ECM Homeostasis in the Nucleus Pulposus Cells
Abstract
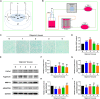
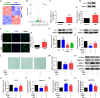
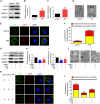
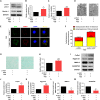
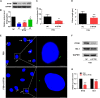
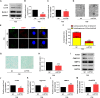
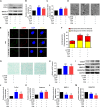
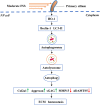
In vertebrate, the nucleus pulposus (NP), which is an essential component of the intervertebral disk, is constantly impacted by fluid shear stress (FSS); however, molecular mechanism(s) through which FSS modulates the NP homeostasis is poorly understood. Here we show that FSS regulates the extracellular matrix (ECM) homeostasis in NP cells. A moderate dose of FSS (i.e., 12 dyne/cm2) increases the sulfated glycosaminoglycan (sGAG) content and protein levels of Col2a1 and Aggrecan and decreases those of matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motif 5 (ADMATS5) in rat NP cells, while a higher dose of FSS (i.e., 24 dyne/cm2) displays opposite effects. Results from RNA sequencing analysis, quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis and western blotting establish that the heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) is a key downstream mediator of the FSS actions in NP cells. HO-1 knockdown abolishes FSS-induced alterations in ECM protein production and sGAG content in NP cells, which is reversed by HO-1 induction. Furthermore, FSS activates the autophagic pathway by increasing the LC3-II/LC3-I ratio, Beclin-1 protein level, and formation of autophagosome and autolysosome and thereby regulates ECM protein and sGAG production in a HO-1 dependent manner. Finally, we demonstrate that the intraflagellar transport (IFT) 88, a core trafficking protein of primary cilia, is critically involved in the HO-1-mediated autophagy activation and ECM protein and sGAG production in FSS-treated NP cells. Thus, we for the first time demonstrate that FSS plays an important role in maintaining ECM homeostasis through HO-1-dependent activation of autophagy in NP cells.
Keywords: autophagy; fluid shear stress; heme oxygenase-1; intraflagellar transport (IFT) 88; nucleus pulposus cell.
Copyright © 2020 Chen, Qin, Wu, Fu, Lin, Chen, Xiao, Shao and Cao.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Periodic Mechanical Stress Induces Extracellular Matrix Expression and Migration of Rat Nucleus Pulposus Cells Through Src-GIT1-ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(4):1510-1521. doi: 10.1159/000494650. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30359987
-
Periodic mechanical stress induces the extracellular matrix expression and migration of rat nucleus pulposus cells by upregulating the expression of intergrin α1 and phosphorylation of downstream phospholipase Cγ1.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Sep;14(3):2457-64. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5549. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27484337 Free PMC article.
-
LIM mineralization protein-1 suppresses TNF-α induced intervertebral disc degeneration by maintaining nucleus pulposus extracellular matrix production and inhibiting matrix metalloproteinases expression.J Orthop Res. 2015 Mar;33(3):294-303. doi: 10.1002/jor.22732. Epub 2014 Oct 21. J Orthop Res. 2015. PMID: 25336289
-
Heme oxygenase-1 attenuates IL-1β induced alteration of anabolic and catabolic activities in intervertebral disc degeneration.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 15;6:21190. doi: 10.1038/srep21190. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26877238 Free PMC article.
-
Heme oxygenase-1 enhances autophagy in podocytes as a protective mechanism against high glucose-induced apoptosis.Exp Cell Res. 2015 Oct 1;337(2):146-59. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.04.005. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25882498 Review.
Cited by
-
Bone-muscle crosstalk under physiological and pathological conditions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jul 27;81(1):310. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05331-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39066929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromium Oxide Nanoparticle Impaired Osteogenesis and Cellular Response to Mechanical Stimulus.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Sep 3;16:6157-6170. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S317430. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34511912 Free PMC article.
-
Kindlin-2 inhibits Nlrp3 inflammasome activation in nucleus pulposus to maintain homeostasis of the intervertebral disc.Bone Res. 2022 Jan 10;10(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s41413-021-00179-5. Bone Res. 2022. PMID: 35013104 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Aerosolization on Endothelial Cells for Efficient Cell Deposition in Biohybrid and Regenerative Applications.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Feb 28;14(3):575. doi: 10.3390/mi14030575. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36984982 Free PMC article.
-
Kindlin-2 regulates skeletal homeostasis by modulating PTH1R in mice.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Dec 26;5(1):297. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00328-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 33361757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An Q. D., Li Y. Y., Zhang H. X., Lu J., Yu X. D., Lin Q., et al. (2018). Inhibition of bromodomain-containing protein 4 ameliorates oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis and cartilage matrix degeneration through activation of NF-E2-related factor 2-heme oxygenase-1 signaling in rat chondrocytes. J. Cell Biochem. 119 7719–7728. 10.1002/jcb.27122 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonnevie E. D., Gullbrand S. E., Ashinsky B. G., Tsinman T. K., Elliott D. M., Chao P. G., et al. (2019). Aberrant mechanosensing in injured intervertebral discs as a result of boundary-constraint disruption and residual-strain loss. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 3 998–1008. 10.1038/s41551-019-0458-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

