Elevated platelet distribution width predicts poor prognosis in hilar cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 32195935
- PMCID: PMC7220385
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019400
Elevated platelet distribution width predicts poor prognosis in hilar cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
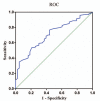
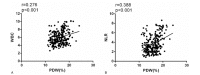
Although the platelet distribution width (PDW) has been reported as a reliable predictor of prognosis in several types of cancer, to our knowledge the prognostic value of PDW in hilar cholangiocarcinoma (HC) has not been studied. The aim of the study was to investigate the prognostic value of PDW in HC patients. A retrospective analysis of 292 consecutively recruited HC patients undergoing radical resection with at least a 5-year follow-up. The optimal cutoff value of PDW was determined by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Survival analysis by the Kaplan-Meier method and the difference between the clinico-pathologic variables and survival was evaluated by log-rank analysis. Multivariate analysis identified independent prognostic risk factors of overall survival (OS). ROC curve analysis suggested that the optimal cutoff value for the PDW was 16.55. There were significant associations of high PDW with high white blood cell (P < .001) and high neutril-to-lymph ratio (P < .001). In a multivariate analysis, the PDW was an independent prognostic factor for overall survival (HR = 2.521, 95% CI 1.832-3.470, P < .001). In conclusions, our findings indicate that PDW may have clinical significance in predicting OS after surgery in HC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Xiong J, Nunes QM, Huang W, et al. Major hepatectomy in Bismuth types I and II hilar cholangiocarcinoma. J Surg Res 2015;194:194–201. - PubMed
-
- Molina V, Sampson J, Ferrer J, et al. Surgical treatment of perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: early results of en bloc portal vein resection. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2017;402:95–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

