A novel cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase gene, TaCRK2, contributes to leaf rust resistance in wheat
- PMID: 32196909
- PMCID: PMC7170779
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12929
A novel cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase gene, TaCRK2, contributes to leaf rust resistance in wheat
Abstract
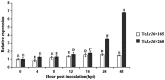
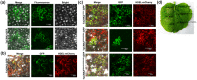
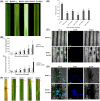
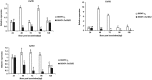
Leaf rust, caused by Puccinia triticina, is one of the most destructive fungal diseases in wheat production worldwide. The hypersensitive reaction (HR) is an important defence response against P. triticina infection. In this study, the physiological races 165 and 260 of P. triticina were combined with a line derived from the bread wheat cultivar Thatcher with the leaf rust resistance locus Lr26 to form compatible and incompatible combinations, respectively. Based on an RNA-Seq database of the interaction systems, a new wheat cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase gene, TaCRK2, is specifically induced and up-regulated in the incompatible combination. We identified that TaCRK2 was regulated in a Ca2+ -dependent manner. Knockdown of TaCRK2 by virus-induced gene silencing and RNAi leads to a dramatic increase in HR area and the number of haustorial mother cells at the single infection site. In addition, urediniospores, a P. triticina-specific pathogenic marker in compatible combinations, were observed on leaf surfaces of silenced plants at approximately 15 days after inoculation in the incompatible combination. Moreover, transcription levels of TaPR1, TaPR2, and TaPR5 were obviously reduced in TaCRK2-silenced plants. TaCRK2 overexpression in Nicotiana benthamiana induced strong HR-like cell death. Finally, transient expression of green fluorescent protein fused with TaCRK2 in N. benthamiana indicated that TaCRK2 localizes in the endoplasmic reticulum. Thus, TaCRK2 plays an important role in the resistance to P. triticina infection and has a positive regulation effect on the HR cell death process induced by P. triticina.
Keywords: Puccinia triticina; VIGS; cysteine-rich receptor-like protein kinase; hypersensitive reaction; wheat.
© 2020 The Authors. Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Translationally controlled tumor protein interacts with TaCIPK23 to positively regulate wheat resistance to Puccinia triticina.Plant J. 2024 Oct;120(1):302-317. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16987. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 39180235
-
Functional characterization of the Wrab17 gene in the interaction process between wheat and Puccinia triticina.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018 Dec;133:100-106. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.10.018. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30399543
-
TaCAMTA4, a Calmodulin-Interacting Protein, Involved in Defense Response of Wheat to Puccinia triticina.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 24;9(1):641. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36385-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30679453 Free PMC article.
-
Wheat leaf rust caused by Puccinia triticina.Mol Plant Pathol. 2008 Sep;9(5):563-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2008.00487.x. Mol Plant Pathol. 2008. PMID: 19018988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The progress of leaf rust research in wheat.Fungal Biol. 2020 Jun;124(6):537-550. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2020.02.013. Epub 2020 Feb 29. Fungal Biol. 2020. PMID: 32448445 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the CRK expressions in bottle gourd (Lagenaria siceraria) under Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lagenariae stress by using genome-wide identification strategy.BMC Genomics. 2025 Mar 3;26(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11349-8. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40033183 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation and Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Fusarium Seedling Blight Resistance in Chinese Elite Wheat Lines.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Nov 17;12:777494. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.777494. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34868179 Free PMC article.
-
The Expression of Triticum aestivum Cysteine-Rich Receptor-like Protein Kinase Genes during Leaf Rust Fungal Infection.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 14;12(16):2932. doi: 10.3390/plants12162932. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631144 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary characteristics, expression patterns of wheat receptor-like kinases and functional analysis of TaCrRLK1L16.Stress Biol. 2025 Apr 3;5(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s44154-025-00215-y. Stress Biol. 2025. PMID: 40178709 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and molecular characterization of CRK gene family in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) under cold stress and sclerotium rolfsii infection.BMC Genomics. 2023 Apr 26;24(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09319-z. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37101152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya, B.R. , Raina, S. , Maqbool, S.B. , Jagadeeswaran, G. , Mosher, S.L. , Appel, H.M. et al (2007) Overexpression of CRK13, an Arabidopsis cysteine‐rich receptor‐like kinase, results in enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas syringae . The Plant Journal, 50, 488–499. - PubMed
-
- Asai, S. and Shirasu, K. (2015) Plant cells under siege: plant immune system versus pathogen effectors. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 28, 1–8. - PubMed
-
- Boller, T. and Felix, G. (2009) A renaissance of elicitors: perception of microbe associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern‐recognition receptors. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 60, 379–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

