Inhibiting ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 N by microRNA-590-3p reduced cell growth of cervical carcinoma
- PMID: 32196955
- PMCID: PMC11896263
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12204
Inhibiting ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 N by microRNA-590-3p reduced cell growth of cervical carcinoma
Abstract
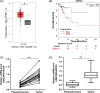
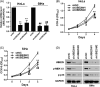
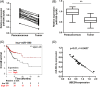
The ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 N (UBE2N) has been reported to be involved in the tumorigenesis of several tumors, but its function in cervical carcinoma has not been investigated yet. In the present study, UBE2N was found elevated in cervical carcinoma, and patients with high UBE2N had a shorter overall survival than patients with low expression. Additionally, knockdown of UBE2N decreased the activation of MEK1/2 and p38 in cervical carcinoma cells, and UBE2N knockdown also markedly inhibited cervical carcinoma cell growth. Our further studies found that microRNA-590-3p (miR-590-3p) was significantly decreased in cervical carcinoma, and patients with high miR-590-3p had a longer overall survival than patients with low expression. Moreover, miR-590-3p expression was found negatively correlated with UBE2N expression in cervical carcinoma, and our further studies showed that miR-590-3p targeted UBE2N and inhibited its expression in cervical carcinoma. Overexpression of miR-590-3p could inhibit cervical carcinoma cell growth, but enhanced UBE2N could rescue miR-590-3p-induced cell growth inhibition in cervical carcinoma. This study indicated that targeting miR-590-3p/UBE2N axis could be a potential strategy for the treatment of cervical carcinoma.
Keywords: UBE2N; cell growth; cervical carcinoma; microRNA-590-3p; target.
© 2020 The Authors. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Yokoi E, Mabuchi S, Takahashi R, Matsumoto Y, Kuroda H, Kozasa K, et al. Impact of histological subtype on survival in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer that were treated with definitive radiotherapy: adenocarcinoma/adenosquamous carcinoma versus squamous cell carcinoma. J Gynecol Oncol. 2017;28:e19. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li N, Tian YW, Xu Y, Meng DD, Gao L, Shen WJ, et al. Combined treatment with autologous CIK cells, radiotherapy and chemotherapy in advanced cervical cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 2019;25:691–696. - PubMed
-
- Diaz Del Arco C, Jimenez Ayala B, Garcia D, Sanabria C, Fernandez Acenero MJ. Distribution of cervical lesions in young and older women. Diagn Cytopathol. 2019;47:659–664. - PubMed

