Vibrational Dynamics of Crystalline 4-Phenylbenzaldehyde from INS Spectra and Periodic DFT Calculations
- PMID: 32197316
- PMCID: PMC7144378
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25061374
Vibrational Dynamics of Crystalline 4-Phenylbenzaldehyde from INS Spectra and Periodic DFT Calculations
Abstract
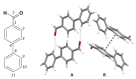
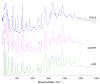
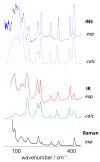
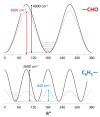
The present work emphasizes the value of periodic density functional theory (DFT) calculations in the assessment of the vibrational spectra of molecular crystals. Periodic calculations provide a nearly one-to-one match between the calculated and observed bands in the inelastic neutron scattering (INS) spectrum of crystalline 4-phenylbenzaldehyde, thus validating their assignment and correcting previous reports based on single molecule calculations. The calculations allow the unambiguous assignment of the phenyl torsional mode at ca. 118-128 cm-1, from which a phenyl torsional barrier of ca. 4000 cm-1 is derived, and the identification of the collective mode involving the antitranslational motion of CH···O bonded pairs, a hallmark vibrational mode of systems where C-H···O contacts are an important feature.
Keywords: C-H···O hydrogen bonds; density functional theory; inelastic neutron scattering; molecular crystal; torsional potential; vibrational assignment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Parker S.F., Butler I.R. Synthesis, Computational Studies, Inelastic Neutron Scattering, Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy of Ruthenocene. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019;2019:1142–1146. doi: 10.1002/ejic.201800914. - DOI
-
- Ribeiro-Claro P.J., Vaz P.D., Nolasco M.M., Araujo C.F., Gil F.P.S.C., Amado A.M. Vibrational dynamics of 4-fluorobenzaldehyde from periodic DFT calculations. Chem. Phys. Lett. X. 2019;2:100006. doi: 10.1016/j.cpletx.2019.100006. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

