Pharmacological Modulation of SAMHD1 Activity by CDK4/6 Inhibitors Improves Anticancer Therapy
- PMID: 32197329
- PMCID: PMC7140116
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12030713
Pharmacological Modulation of SAMHD1 Activity by CDK4/6 Inhibitors Improves Anticancer Therapy
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Castellví, M. et al. Pharmacological Modulation of SAMHD1 Activity by CDK4/6 Inhibitors Improves Anticancer Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 713.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 29;12(7):1728. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071728. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32610575 Free PMC article.
Abstract
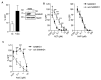
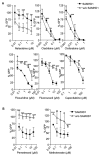
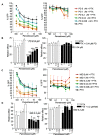
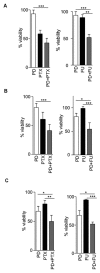
Sterile alpha motif and histidine-aspartic acid domain-containing protein 1 (SAMHD1) is a dNTP triphosphohydrolase involved in the regulation of the intracellular dNTP pool, linked to viral restriction, cancer development and autoimmune disorders. SAMHD1 function is regulated by phosphorylation through a mechanism controlled by cyclin-dependent kinases and tightly linked to cell cycle progression. Recently, SAMHD1 has been shown to decrease the efficacy of nucleotide analogs used as chemotherapeutic drugs. Here, we demonstrate that SAMHD1 can enhance or decrease the efficacy of various classes of anticancer drug, including nucleotide analogues, but also anti-folate drugs and CDK inhibitors. Importantly, we show that selective CDK4/6 inhibitors are pharmacological activators of SAMHD1 that act by inhibiting its inactivation by phosphorylation. Combinations of a CDK4/6 inhibitor with nucleoside or folate antimetabolites potently enhanced drug efficacy, resulting in highly synergic drug combinations (CI < 0.04). Mechanistic analyses reveal that cell cycle-controlled modulation of SAMHD1 function is the central process explaining changes in anticancer drug efficacy, therefore providing functional proof of the potential of CDK4/6 inhibitors as a new class of adjuvants to boost chemotherapeutic regimens. The evaluation of SAMHD1 expression in cancer tissues allowed for the identification of cancer types that would benefit from the pharmacological modulation of SAMHD1 function. In conclusion, these results indicate that the modulation of SAMHD1 function may represent a promising strategy for the improvement of current antimetabolite-based treatments.
Keywords: CDK4/6; HIV; SAMHD1; antimetabolite; cancer; pemetrexed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Franzolin E., Pontarin G., Rampazzo C., Miazzi C., Ferraro P., Palumbo E., Reichard P., Bianchi V. The deoxynucleotide triphosphohydrolase SAMHD1 is a major regulator of DNA precursor pools in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:14272–14277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312033110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rice G.I., Bond J., Asipu A., Brunette R.L., Manfield I.W., Carr I.M., Fuller J.C., Jackson R.M., Lamb T., Briggs T.A., et al. Mutations involved in Aicardi-Goutières syndrome implicate SAMHD1 as regulator of the innate immune response. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:829–832. doi: 10.1038/ng.373. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clifford R., Louis T., Robbe P., Ackroyd S., Burns A., Timbs A.T., Wright Colopy G., Dreau H., Sigaux F., Judde J.G., et al. SAMHD1 is mutated recurrently in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is involved in response to DNA damage. Blood. 2014;123:1021–1031. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-04-490847. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rentoft M., Lindell K., Tran P., Chabes A.L., Buckland R.J., Watt D.L., Marjavaara L., Nilsson A.K., Melin B., Trygg J., et al. Heterozygous colon cancer-associated mutations of SAMHD1 have functional significance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113:4723–4728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1519128113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

