MicroRNA (miRNA): A New Dimension in the Pathogenesis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS)
- PMID: 32197340
- PMCID: PMC7139820
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21062076
MicroRNA (miRNA): A New Dimension in the Pathogenesis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS)
Abstract
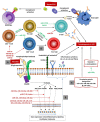
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are single-stranded, endogenous RNA molecules that play a significant role in the regulation of gene expression as well as cell development, differentiation, and function. Recent data suggest that these small molecules are responsible for the regulation of immune responses. Therefore, they may act as potent modulators of the immune system and play an important role in the development of several autoimmune diseases. Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune systemic disease characterized by venous and/or arterial thromboses and/or recurrent fetal losses in the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLs). Several lines of evidence suggest that like other autoimmune disorders, miRNAs are deeply involved in the pathogenesis of APS, interacting with the function of innate and adaptive immune responses. In this review, we characterize miRNAs in the light of having a functional role in the immune system and autoimmune responses focusing on APS. In addition, we also discuss miRNAs as potential biomarkers and target molecules in treating APS.
Keywords: APS; MicroRNA; antiphospholipid syndrome; autoimmunity; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

