Claudin-12 Knockout Mice Demonstrate Reduced Proximal Tubule Calcium Permeability
- PMID: 32197346
- PMCID: PMC7139911
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21062074
Claudin-12 Knockout Mice Demonstrate Reduced Proximal Tubule Calcium Permeability
Abstract
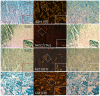
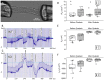
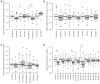
The renal proximal tubule (PT) is responsible for the reabsorption of approximately 65% of filtered calcium, primarily via a paracellular pathway. However, which protein(s) contribute this paracellular calcium pore is not known. The claudin family of tight junction proteins confers permeability properties to an epithelium. Claudin-12 is expressed in the kidney and when overexpressed in cell culture contributes paracellular calcium permeability (PCa). We therefore examined claudin-12 renal localization and its contribution to tubular paracellular calcium permeability. Claudin-12 null mice (KO) were generated by replacing the single coding exon with β-galactosidase from Escherichia coli. X-gal staining revealed that claudin-12 promoter activity colocalized with aquaporin-1, consistent with the expression in the PT. PTs were microperfused ex vivo and PCa was measured. PCa in PTs from KO mice was significantly reduced compared with WT mice. However, urinary calcium excretion was not different between genotypes, including those on different calcium containing diets. To assess downstream compensation, we examined renal mRNA expression. Claudin-14 expression, a blocker of PCa in the thick ascending limb (TAL), was reduced in the kidney of KO animals. Thus, claudin-12 is expressed in the PT, where it confers paracellular calcium permeability. In the absence of claudin-12, reduced claudin-14 expression in the TAL may compensate for reduced PT calcium reabsorption.
Keywords: calcium permeability; claudin-12; proximal tubule.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Combinatorial expression of claudins in the proximal renal tubule and its functional consequences.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 May 1;318(5):F1138-F1146. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00057.2019. Epub 2020 Mar 16. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32174144 Free PMC article.
-
Claudins and nephrolithiasis.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2018 Jul;27(4):268-276. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000426. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2018. PMID: 29782346 Review.
-
Interaction between Epithelial Sodium Channel γ-Subunit and Claudin-8 Modulates Paracellular Sodium Permeability in Renal Collecting Duct.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 May;31(5):1009-1023. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019080790. Epub 2020 Apr 3. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32245797 Free PMC article.
-
Axial heterogeneity of superficial proximal tubule paracellular transport in mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Dec 1;327(6):F1067-F1078. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00187.2024. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39480273
-
Claudins in barrier and transport function-the kidney.Pflugers Arch. 2017 Jan;469(1):105-113. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1906-6. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Pflugers Arch. 2017. PMID: 27878608 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced Claudin-12 Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis in Cervical Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 6;22(7):3774. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073774. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33917356 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic changes in kidney stone disease.Front Immunol. 2023 May 9;14:1142207. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1142207. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37228601 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Type-Specific Gene Expression in Developing Mouse Neocortex: Intermediate Progenitors Implicated in Axon Development.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Jul 12;14:686034. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.686034. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34321999 Free PMC article.
-
Tight Junction Modulating Bioprobes for Drug Delivery System to the Brain: A Review.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Dec 19;12(12):1236. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12121236. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33352631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary sodium wasting and disrupted collecting duct function in mice with distal renal tubular acidosis mutations.Dis Model Mech. 2025 May 1;18(5):dmm052138. doi: 10.1242/dmm.052138. Epub 2025 May 23. Dis Model Mech. 2025. PMID: 40289527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pan W., Borovac J., Spicer Z., Hoenderop J.G., Bindels R.J., Shull G.E., Doschak M.R., Cordat E., Alexander R.T. The epithelial sodium/proton exchanger, NHE3, is necessary for renal and intestinal calcium (re)absorption. Am. J. Physiol. 2012;302:F943–F956. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00504.2010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

