A Defect in Thymic Tolerance Causes T Cell-Mediated Autoimmunity in a Murine Model of COPA Syndrome
- PMID: 32198142
- PMCID: PMC7324259
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000028
A Defect in Thymic Tolerance Causes T Cell-Mediated Autoimmunity in a Murine Model of COPA Syndrome
Abstract
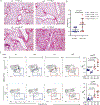
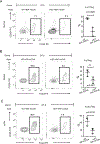
COPA syndrome is a recently described Mendelian autoimmune disorder caused by missense mutations in the coatomer protein complex subunit α (COPA) gene. Patients with COPA syndrome develop arthritis and lung disease that presents as pulmonary hemorrhage or interstitial lung disease (ILD). Immunosuppressive medications can stabilize the disease, but many patients develop progressive pulmonary fibrosis, which requires life-saving measures, such as lung transplantation. Because very little is understood about the pathogenesis of COPA syndrome, it has been difficult to devise effective treatments for patients. To date, it remains unknown which cell types are critical for mediating the disease as well as the mechanisms that lead to autoimmunity. To explore these issues, we generated a CopaE241K/+ germline knock-in mouse bearing one of the same Copa missense mutations in patients. Mutant mice spontaneously developed ILD that mirrors lung pathology in patients, as well as elevations of activated cytokine-secreting T cells. In this study, we show that mutant Copa in epithelial cells of the thymus impairs the thymic selection of T cells and results in both an increase in autoreactive T cells and decrease in regulatory T cells in peripheral tissues. We demonstrate that T cells from CopaE241K/+ mice are pathogenic and cause ILD through adoptive transfer experiments. In conclusion, to our knowledge, we establish a new mouse model of COPA syndrome to identify a previously unknown function for Copa in thymocyte selection and demonstrate that a defect in central tolerance is a putative mechanism by which COPA mutations lead to autoimmunity in patients.
Copyright © 2020 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures




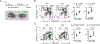


References
-
- Watkin LB, Jessen B, Wiszniewski W, Vece TJ, Jan M, Sha Y, Thamsen M, Santos-Cortez RLP, Lee K, Gambin T, Forbes LR, Law CS, Stray-Pedersen A, Cheng MH, Mace EM, Anderson MS, Liu D, Tang LF, Nicholas SK, Nahmod K, Makedonas G, Canter DL, Kwok P-Y, Hicks J, Jones KD, Penney S, Jhangiani SN, Rosenblum MD, Dell SD, Waterfield MR, Papa FR, Muzny DM, Zaitlen N, Leal SM, Gonzaga-Jauregui C, Baylor-Hopkins Center for Mendelian Genomics, Boerwinkle E, Eissa NT, Gibbs RA, Lupski JR, Orange JS, and Shum AK. 2015. COPA mutations impair ER-Golgi transport and cause hereditary autoimmune-mediated lung disease and arthritis. Nature genetics 47: 654–660. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tsui JL, Estrada OA, Deng Z, Wang KM, Law CS, Elicker BM, Jones KD, Dell SD, Gudmundsson G, Hansdottir S, Helfgott SM, Volpi S, Gattorno M, Waterfield MR, Chan AY, Chung SA, Ley B, and Shum AK. 2018. Analysis of pulmonary features and treatment approaches in the COPA syndrome. ERJ Open Research 4: 00017–2018. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fish F, and Ziff M. 1981. A sensitive solid phase microradioimmunoassay for anti-double stranded DNA antibodies. Arthritis Rheum 24: 534–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

