Integrated Pancreatic Blood Flow: Bidirectional Microcirculation Between Endocrine and Exocrine Pancreas
- PMID: 32198213
- PMCID: PMC7306124
- DOI: 10.2337/db19-1034
Integrated Pancreatic Blood Flow: Bidirectional Microcirculation Between Endocrine and Exocrine Pancreas
Abstract
The pancreatic islet is a highly vascularized endocrine micro-organ. The unique architecture of rodent islets, a so-called core-mantle arrangement seen in two-dimensional images, led researchers to seek functional implications for islet hormone secretion. Three models of islet blood flow were previously proposed, all based on the assumption that islet microcirculation occurs in an enclosed structure. Recent electrophysiological and molecular biological studies using isolated islets also presumed unidirectional flow. Using intravital analysis of the islet microcirculation in mice, we found that islet capillaries were continuously integrated to those in the exocrine pancreas, which made the islet circulation rather open, not self-contained. Similarly in human islets, the capillary structure was integrated with pancreatic microvasculature in its entirety. Thus, islet microcirculation has no relation to islet cytoarchitecture, which explains its well-known variability throughout species. Furthermore, tracking fluorescent-labeled red blood cells at the endocrine-exocrine interface revealed bidirectional blood flow, with similar variability in blood flow speed in both the intra- and extra-islet vasculature. To date, the endocrine and exocrine pancreas have been studied separately by different fields of investigators. We propose that the open circulation model physically links both endocrine and exocrine parts of the pancreas as a single organ through the integrated vascular network.
© 2020 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
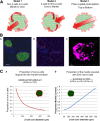
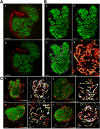
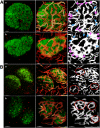




Comment in
-
Blood Flow in the Pancreatic Islet: Not so Isolated Anymore.Diabetes. 2020 Jul;69(7):1336-1338. doi: 10.2337/dbi20-0016. Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32561621 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Orci L, Unger RH. Functional subdivision of islets of Langerhans and possible role of D cells. Lancet 1975;2:1243–1244 - PubMed
-
- Brunicardi FC, Stagner J, Bonner-Weir S, et al. .; Long Beach Veterans Administration Regional Medical Education Center Symposium . Microcirculation of the islets of Langerhans. Diabetes 1996;45:385–392 - PubMed
-
- McCuskey RS, Chapman TM. Microscopy of the living pancreas in situ. Am J Anat 1969;126:395–407 - PubMed
-
- Bonner-Weir S, Orci L. New perspectives on the microvasculature of the islets of Langerhans in the rat. Diabetes 1982;31:883–889 - PubMed

