Perioperative Transfusions and Venous Thromboembolism
- PMID: 32198293
- PMCID: PMC7111487
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2019-2351
Perioperative Transfusions and Venous Thromboembolism
Abstract
Background and objectives: Annual incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) including postoperative VTE in hospitalized children is rising significantly. A growing body of evidence supports the role of red blood cells (RBCs) in pathologic thrombosis. In this study, we examined the association of perioperative RBC transfusion with postoperative VTE in pediatric patients.
Methods: The pediatric databases of the American College of Surgeons' National Surgical Quality Improvement Project from 2012 to 2017 were used. Multivariable logistic regression was used to examine the association between perioperative RBC transfusion status and the development of new or progressive VTE within 30 days of surgery. The analyses were age stratified, as follows: neonates (≤28 days), infants (>28 days and <1 year), and children (≥1 year).
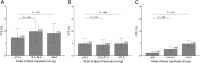
Results: In this study, we included 20 492 neonates, 79 744 infants, and 382 862 children. Postoperative development of VTE was reported in 99 (0.48%) neonates, 147 (0.2%) infants, and 374 (0.1%) children. In all age groups, development of VTE was significantly more common among patients with a perioperative RBC transfusion than patients without a perioperative RBC transfusion (neonates: adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 4.1, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 2.5-6.7; infants: aOR = 2.4, 95% CI = 1.7-3.6; children: aOR = 2.2, 95% CI = 1.7-2.9). Among children who received an intra- or postoperative transfusion, the weight-based volume of RBCs (mL/kg) transfused was associated with postoperative VTE in a dose-dependent manner: second tertile (odds ratio = 2.3, 95% CI = 1.3-4.1) and third tertile (odds ratio = 4.1, 95% CI = 2.3-7.4) versus first tertile.
Conclusions: Perioperative RBC transfusions are independently associated with development of new or progressive postoperative VTE in children, infants, and neonates. These findings need further validation in prospective studies and emphasize the need for evidence-based perioperative pediatric blood transfusion decisions.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Comment in
-
Red Cell Transfusion and Thrombotic Risk in Children.Pediatrics. 2020 Apr;145(4):e20193955. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3955. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Pediatrics. 2020. PMID: 32198294 No abstract available.
References
-
- Raffini L, Huang YS, Witmer C, Feudtner C. Dramatic increase in venous thromboembolism in children’s hospitals in the United States from 2001 to 2007. Pediatrics. 2009;124(4):1001–1008 - PubMed
-
- Goudie A, Dynan L, Brady PW, Fieldston E, Brilli RJ, Walsh KE. Costs of venous thromboembolism, catheter-associated urinary tract infection, and pressure ulcer. Pediatrics. 2015;136(3):432–439 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

