Long noncoding RNA AGPG regulates PFKFB3-mediated tumor glycolytic reprogramming
- PMID: 32198345
- PMCID: PMC7083971
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15112-3
Long noncoding RNA AGPG regulates PFKFB3-mediated tumor glycolytic reprogramming
Abstract
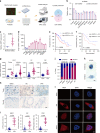
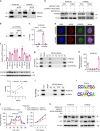
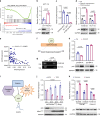
Tumor cells often reprogram their metabolism for rapid proliferation. The roles of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in metabolism remodeling and the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Through screening, we found that the lncRNA Actin Gamma 1 Pseudogene (AGPG) is required for increased glycolysis activity and cell proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Mechanistically, AGPG binds to and stabilizes 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3). By preventing APC/C-mediated ubiquitination, AGPG protects PFKFB3 from proteasomal degradation, leading to the accumulation of PFKFB3 in cancer cells, which subsequently activates glycolytic flux and promotes cell cycle progression. AGPG is also a transcriptional target of p53; loss or mutation of TP53 triggers the marked upregulation of AGPG. Notably, inhibiting AGPG dramatically impaired tumor growth in patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models. Clinically, AGPG is highly expressed in many cancers, and high AGPG expression levels are correlated with poor prognosis, suggesting that AGPG is a potential biomarker and cancer therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Significance of long non-coding RNA AGPG for the metabolism of esophageal cancer.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020 Jul;40(7):313-315. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12035. Epub 2020 May 25. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32449319 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

