NELL2-Robo3 complex structure reveals mechanisms of receptor activation for axon guidance
- PMID: 32198364
- PMCID: PMC7083938
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15211-1
NELL2-Robo3 complex structure reveals mechanisms of receptor activation for axon guidance
Abstract
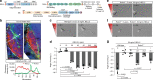
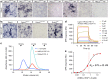
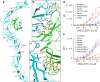
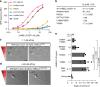
Axon pathfinding is critical for nervous system development, and it is orchestrated by molecular cues that activate receptors on the axonal growth cone. Robo family receptors bind Slit guidance cues to mediate axon repulsion. In mammals, the divergent family member Robo3 does not bind Slits, but instead signals axon repulsion from its own ligand, NELL2. Conversely, canonical Robos do not mediate NELL2 signaling. Here, we present the structures of NELL-Robo3 complexes, identifying a mode of ligand engagement for Robos that is orthogonal to Slit binding. We elucidate the structural basis for differential binding between NELL and Robo family members and show that NELL2 repulsive activity is a function of its Robo3 affinity and is enhanced by ligand trimerization. Our results reveal a mechanism of oligomerization-induced Robo activation for axon guidance and shed light on Robo family member ligand binding specificity, conformational variability, divergent modes of signaling, and evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glu592 of the axon guidance receptor ROBO3 mediates a pH-dependent interaction with NELL2 ligand.FEBS Lett. 2025 Feb;599(4):571-580. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.15054. Epub 2024 Nov 12. FEBS Lett. 2025. PMID: 39531524 Free PMC article.
-
Operational redundancy in axon guidance through the multifunctional receptor Robo3 and its ligand NELL2.Science. 2015 Nov 20;350(6263):961-5. doi: 10.1126/science.aad2615. Science. 2015. PMID: 26586761
-
Robo recruitment of the Wave regulatory complex plays an essential and conserved role in midline repulsion.Elife. 2021 Apr 12;10:e64474. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64474. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33843588 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular Trafficking Mechanisms that Regulate Repulsive Axon Guidance.Neuroscience. 2023 Jan 1;508:123-136. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.07.012. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Neuroscience. 2023. PMID: 35863679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Slit-Robo signaling.Development. 2016 Sep 1;143(17):3037-44. doi: 10.1242/dev.132829. Development. 2016. PMID: 27578174 Review.
Cited by
-
Dorsal commissural axon guidance in the developing spinal cord.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2021;142:197-231. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2020.10.009. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33706918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robo functions as an attractive cue for glial migration through SYG-1/Neph.Elife. 2020 Nov 19;9:e57921. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57921. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33211005 Free PMC article.
-
A cis-regulatory module underlies retinal ganglion cell genesis and axonogenesis.Cell Rep. 2024 Jun 25;43(6):114291. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114291. Epub 2024 May 31. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38823017 Free PMC article.
-
Glu592 of the axon guidance receptor ROBO3 mediates a pH-dependent interaction with NELL2 ligand.FEBS Lett. 2025 Feb;599(4):571-580. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.15054. Epub 2024 Nov 12. FEBS Lett. 2025. PMID: 39531524 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Slit Ligands and Their Roundabout (Robo) Family of Receptors in Bone Remodeling.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;21:143-154. doi: 10.1007/5584_2020_586. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 32986130 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

