Self-assembly of robust gold nanoparticle monolayer architectures for quantitative protein interaction analysis by LSPR spectroscopy
- PMID: 32198532
- PMCID: PMC7214499
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-020-02551-6
Self-assembly of robust gold nanoparticle monolayer architectures for quantitative protein interaction analysis by LSPR spectroscopy
Abstract
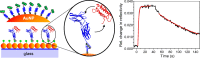
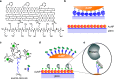
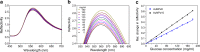
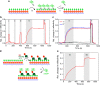
Localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) detection offers highly sensitive label-free detection of biomolecular interactions. Simple and robust surface architectures compatible with real-time detection in a flow-through system are required for broad application in quantitative interaction analysis. Here, we established self-assembly of a functionalized gold nanoparticle (AuNP) monolayer on a glass substrate for stable, yet reversible immobilization of Histidine-tagged proteins. To this end, one-step coating of glass substrates with poly-L-lysine graft poly(ethylene glycol) functionalized with ortho-pyridyl disulfide (PLL-PEG-OPSS) was employed as a reactive, yet biocompatible monolayer to self-assemble AuNP into a LSPR active monolayer. Site-specific, reversible immobilization of His-tagged proteins was accomplished by coating the AuNP monolayer with tris-nitrilotriacetic acid (trisNTA) PEG disulfide. LSPR spectroscopy detection of protein binding on these biocompatible functionalized AuNP monolayers confirms high stability under various harsh analytical conditions. These features were successfully employed to demonstrate unbiased kinetic analysis of cytokine-receptor interactions. Graphical abstract.
Keywords: Kinetics; Localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR); Protein immobilization; Quantitative interaction analysis; Real-time biosensor; Self-assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Willets KA, Duyne RPV. Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and sensing. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 2007;58(1):267–297. - PubMed
-
- Bhagawati M, You C, Piehler J. Quantitative real-time imaging of protein–protein interactions by LSPR detection with micropatterned gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2013;85(20):9564–9571. - PubMed
-
- Matricardi C, Hanske C, Garcia-Pomar JL, Langer J, Mihi A, Liz-Marzán LM. Gold nanoparticle plasmonic superlattices as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrates. ACS Nano. 2018;12(8):8531–8539. - PubMed
-
- Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, Van Duyne RP. Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater. 2008;7(6):442–453. - PubMed
-
- Jackman JA, Rahim Ferhan A, Cho NJ. Nanoplasmonic sensors for biointerfacial science. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46(12):3615–3660. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

