Alzheimer's Risk Factors Age, APOE Genotype, and Sex Drive Distinct Molecular Pathways
- PMID: 32199103
- PMCID: PMC7388065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.02.034
Alzheimer's Risk Factors Age, APOE Genotype, and Sex Drive Distinct Molecular Pathways
Abstract
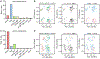
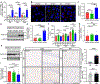
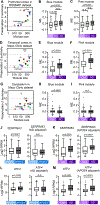
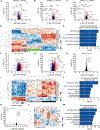
Evidence suggests interplay among the three major risk factors for Alzheimer's disease (AD): age, APOE genotype, and sex. Here, we present comprehensive datasets and analyses of brain transcriptomes and blood metabolomes from human apoE2-, apoE3-, and apoE4-targeted replacement mice across young, middle, and old ages with both sexes. We found that age had the greatest impact on brain transcriptomes highlighted by an immune module led by Trem2 and Tyrobp, whereas APOE4 was associated with upregulation of multiple Serpina3 genes. Importantly, these networks and gene expression changes were mostly conserved in human brains. Finally, we observed a significant interaction between age, APOE genotype, and sex on unfolded protein response pathway. In the periphery, APOE2 drove distinct blood metabolome profile highlighted by the upregulation of lipid metabolites. Our work identifies unique and interactive molecular pathways underlying AD risk factors providing valuable resources for discovery and validation research in model systems and humans.
Keywords: APOE; Alzheimer’s disease; Serpina3; age; extracellular vesicles; inflammation; lipid metabolism; metabolomics; sex; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests M.A. is co-inventor on patent WO2018049268 in this field. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham CR, McGraw WT, Slot F, and Yamin R (2000). Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin inhibits A beta degradation in vitro and in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci 920, 245–248. - PubMed
-
- Abraham CR, Selkoe DJ, and Potter H (1988). Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 52, 487–501. - PubMed
-
- Abraham CR, Shirahama T, and Potter H (1990). Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin is associated solely with amyloid deposits containing the beta-protein. Amyloid and cell localization of alpha 1-antichymotrypsin. Neurobiol Aging 11, 123–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS074969/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG051504/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG062110/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS080820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG046205/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG061359/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017216/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG046171/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG035355/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027924/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA200572/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061796/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032990/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AG051356/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG027924/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS072026/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG066395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025711/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057181/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG052423/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG056130/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG051550/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

