Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19
- PMID: 32199493
- PMCID: PMC7158902
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30232-2
Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19
Figures
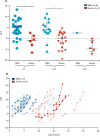
References
-
- WHO Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in suspected human cases. 2020. https://www.who.int/publications-detail/laboratory-testing-for-2019-nove...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

