Capturing functional epigenomes for insight into metabolic diseases
- PMID: 32199819
- PMCID: PMC7300388
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.12.016
Capturing functional epigenomes for insight into metabolic diseases
Abstract
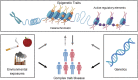
Background: Metabolic diseases such as obesity are known to be driven by both environmental and genetic factors. Although genome-wide association studies of common variants and their impact on complex traits have provided some biological insight into disease etiology, identified genetic variants have been found to contribute only a small proportion to disease heritability, and to map mainly to non-coding regions of the genome. To link variants to function, association studies of cellular traits, such as epigenetic marks, in disease-relevant tissues are commonly applied.
Scope of the review: We review large-scale efforts to generate genome-wide maps of coordinated epigenetic marks and their utility in complex disease dissection with a focus on DNA methylation. We contrast DNA methylation profiling methods and discuss the advantages of using targeted methods for single-base resolution assessments of methylation levels across tissue-specific regulatory regions to deepen our understanding of contributing factors leading to complex diseases.
Major conclusions: Large-scale assessments of DNA methylation patterns in metabolic disease-linked study cohorts have provided insight into the impact of variable epigenetic variants in disease etiology. In-depth profiling of epigenetic marks at regulatory regions, particularly at tissue-specific elements, will be key to dissect the genetic and environmental components contributing to metabolic disease onset and progression.
Keywords: Adipose tissue; DNA methylation; Epigenomics; Metabolic diseases; Next-generation sequencing; Regulatory elements.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dissecting features of epigenetic variants underlying cardiometabolic risk using full-resolution epigenome profiling in regulatory elements.Nat Commun. 2019 Mar 14;10(1):1209. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09184-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30872577 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenome-Wide Association Study Identifies Cardiac Gene Patterning and a Novel Class of Biomarkers for Heart Failure.Circulation. 2017 Oct 17;136(16):1528-1544. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027355. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28838933
-
Tools and Strategies for Analysis of Genome-Wide and Gene-Specific DNA Methylation Patterns.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1537:249-277. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6685-1_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27924599 Review.
-
Functional variation in allelic methylomes underscores a strong genetic contribution and reveals novel epigenetic alterations in the human epigenome.Genome Biol. 2017 Mar 10;18(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1173-7. Genome Biol. 2017. PMID: 28283040 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin Profiling Techniques: Exploring the Chromatin Environment and Its Contributions to Complex Traits.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 16;22(14):7612. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147612. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299232 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative Analysis of Glucometabolic Traits, Adipose Tissue DNA Methylation, and Gene Expression Identifies Epigenetic Regulatory Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance and Obesity in African Americans.Diabetes. 2020 Dec;69(12):2779-2793. doi: 10.2337/db20-0117. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32928872 Free PMC article.
-
Overweight and obesity in pregnancy: their impact on epigenetics.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2021 Dec;75(12):1710-1722. doi: 10.1038/s41430-021-00905-6. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34230629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylome in visceral adipose tissue can discriminate patients with and without colorectal cancer.Epigenetics. 2022 Jun;17(6):665-676. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2021.1950991. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 34311674 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic pathways, genomic alterations, and post-translational modifications in pulmonary hypertension and cancer as therapeutic targets and biomarkers.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 20;15:1490892. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1490892. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39635438 Free PMC article.
-
Role of long non-coding RNAs in adipogenesis: State of the art and implications in obesity and obesity-associated diseases.Obes Rev. 2021 Jul;22(7):e13203. doi: 10.1111/obr.13203. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Obes Rev. 2021. PMID: 33443301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kilpinen H., Dermitzakis E.T. Genetic and epigenetic contribution to complex traits. Human Molecular Genetics. 2012;21(R1):R24–R28. - PubMed
-
- Barres R., Zierath J.R. DNA methylation in metabolic disorders. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2011;93(4):897S–900S. - PubMed
-
- Gluckman P.D., Hanson M.A., Buklijas T., Low F.M., Beedle A.S. Epigenetic mechanisms that underpin metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 2009;5(7):401–408. - PubMed
-
- McCarthy M.I. Genomics, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. New England Journal of Medicine. 2010;363(24):2339–2350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

